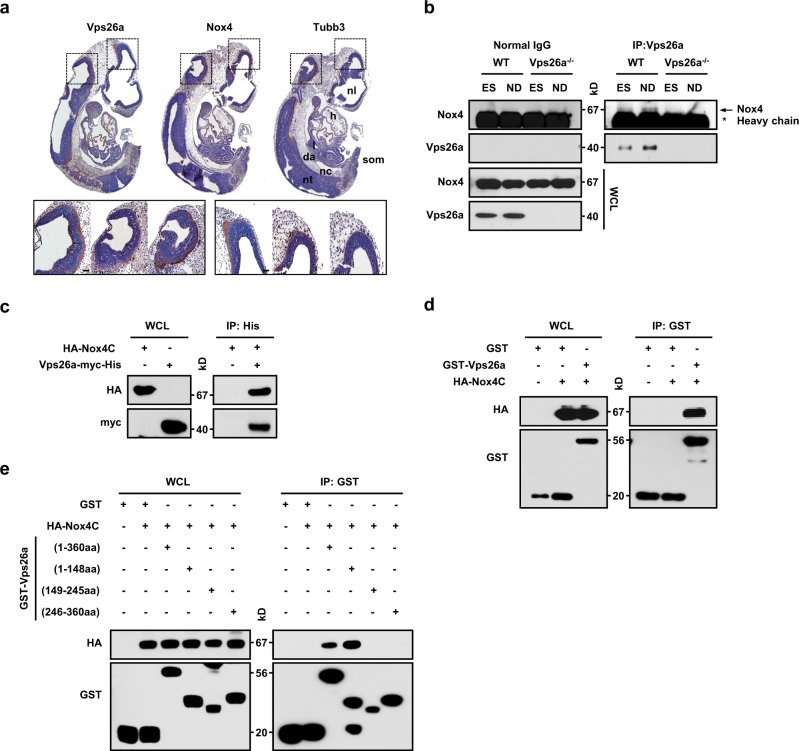
Fig. 6.
Identification of the interaction between Vps26a and Nox4. a Serial sagittal sections of WT embryos were immunostained for Vps26a, Nox4, and Tubb3 and counterstained lightly with hematoxylin at E10.5. da, dorsal aorta; l, lung; h, heart; nc, notochord; nl, neural lumen; nt, neural tube; som, somite. b Vps26a immunoprecipitation followed by anti-Vps26a and -Nox4 immunoblots using lysates obtained from WT (+/+) and Vps26a-/- (-/-) ESCs during neural differentiation for 0 or 6 days. IgG was used as an immunoprecipitation control. c GST-tagged Vps26a was subjected to a pull-down assay with the lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with HA-Nox4C (C-terminal region, 249–574 aa)-expressing plasmid. Immunoblot analysis with anti-HA antibody is shown at the top. Equal loading of the GST proteins assessed by GST antibody is shown at the bottom. GST was used as a negative control. d Cell lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with HA-Nox4C were mixed with purified His-tagged Vps26a. Samples were immunoblotted with the HA tag antibody. Levels of input protein are shown by immunoblotting with the HA- and Myc-tag antibodies. e Expression constructs for GST-tagged serial deletion mutants of Vps26a and HA-Nox4C were co-expressed in HEK293 cells. Immunoblot analysis with anti-HA antibody is shown at the top. Equal loading of the GST proteins assessed by GST antibody is shown at the bottom. GST was used as a negative control