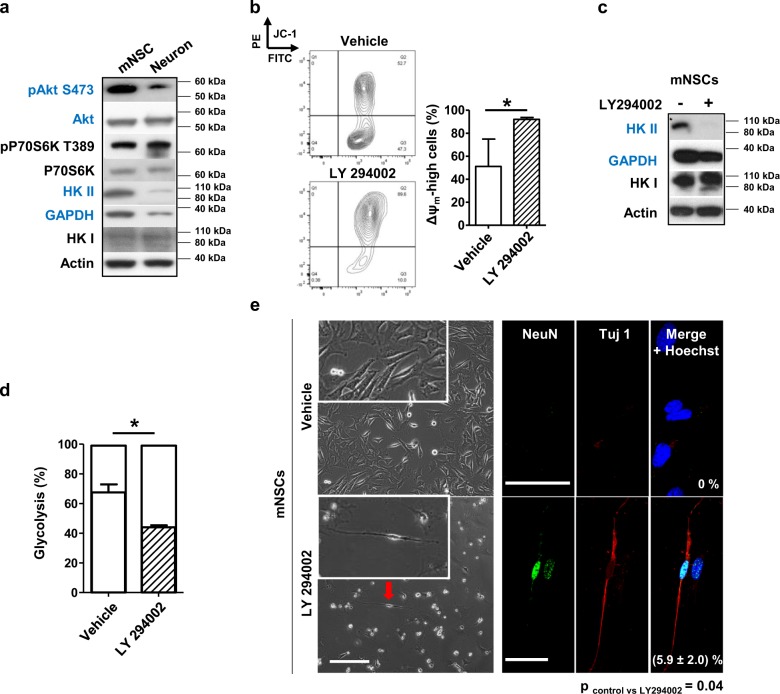
Fig. 4.
PI3K signaling is reduced in differentiated neurons as compared to mNSCs. Inhibition of PI3K increases the Δψm, diminishes the reliance on glycolysis and induces neuronal differentiation of mNSCs. a Total cell lysates of mNSCs and differentiated neurons were prepared for Western blot analysis. PI3K signaling and proteins associated with glycolysis were investigated. b mNSCs were cultured in stem cell medium in the presence or absence of LY294002 (1 µM) for 4 days and mitochondrial polarization was examined by JC-1 staining with FACS. The Δψm-high cell subpopulation was quantified and data are presented in the bar diagram on the right. Data shown are means ± SDs of 3 independent experiments. An unpaired, two-tailed Student's t test was performed. c mNSCs were cultured in the presence or absence of LY294002 (1 µM) for 4 days. Cell lysates were collected for Western blot analysis. d mNSCs were cultured in stem cell medium in the presence or absence of LY294002 (1 µM) for 4 days. Glucose consumption and lactate production were measured and the bioenergetic profiles of the cells were calculated as described in the Materials and Methods. Data shown are means ± SDs of 3 independent experiments. An unpaired, two-tailed student t test was performed. e mNSCs were cultured in stem cell medium in the presence or absence of LY294002 (1 µM) for 4 days. Neuronal markers, NeuN and Tuj1 were stained and images obtained by confocal microscopy. NeuN and Tuj1 double positive neurons were calculated as a percentage of the total cell number by evaluating more than 5 images per condition of 3 independent experiments. An unpaired, two-tailed student t test was performed. Scale bars: 200 µm (phase contrast images) and 50 µm (confocal images)