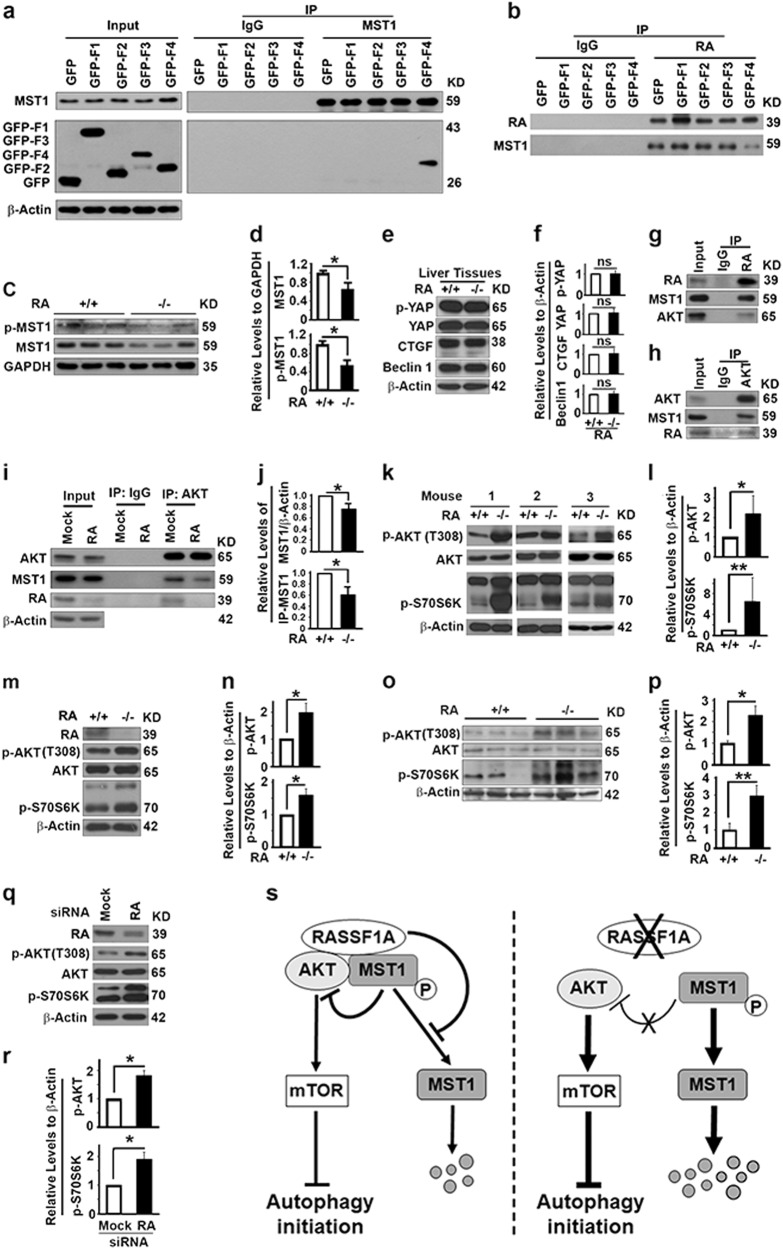
Fig. 5.
RASSF1A suppresses PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway to promote autophagy initiation through Hippo pathway regulatory protein MST1. a Representative immunoblots showing the fragment of RASSF1A coimmunoprecipitated with MST1 in 293T cells. b Representative immunoblots showing the impact of fragments of RASSF1A on the amount of MST1 coimmunoprecipitated with RASSF1A in 293T cells. Inputs are the same as in panel a. c, d Representative immunoblots (c) and quantification showing the impact of RASSF1A on levels of total and p-MST1 (d) in mouse liver tissues. e, f Representative immunoblots (e) and quantification (f) showing the impact of RASSF1A on levels of p-YAP, YAP, CTGF and Beclin 1 in mouse liver tissues. g, h Representative immunoblots showing levels of MST1 and Akt coimmunoprecipitated with RASSF1A (g) or levels of MST1 and RASSF1A coimmunoprecipitated with Akt (h) in HeLa cells. I, j Representative immunoblots (i) and quantification showing the impact of RASSF1A suppression on the levels of total MST1 or MST1 coimmunoprecipitated (IP-MST1) with Akt (j) in HeLa cells treated with random (Mock) or RASSF1A-specific siRNAs. k–r Representative immunoblots (k, m, o, q) and quantification showing the levels of p-AKT and p-S70S6K (l, n, p, r) in mouse liver tissues (k, l), MEFs (m, n), liver tissues from DEN-treated 6-month-old mice (o, p), or HeLa cells treated with random (Mock) or RASSF1A-specific siRNAs (q, r). s A diagram showing the mechanism by which RASSF1A promotes autophagy initiation through MST1-AKT-mTOR pathway