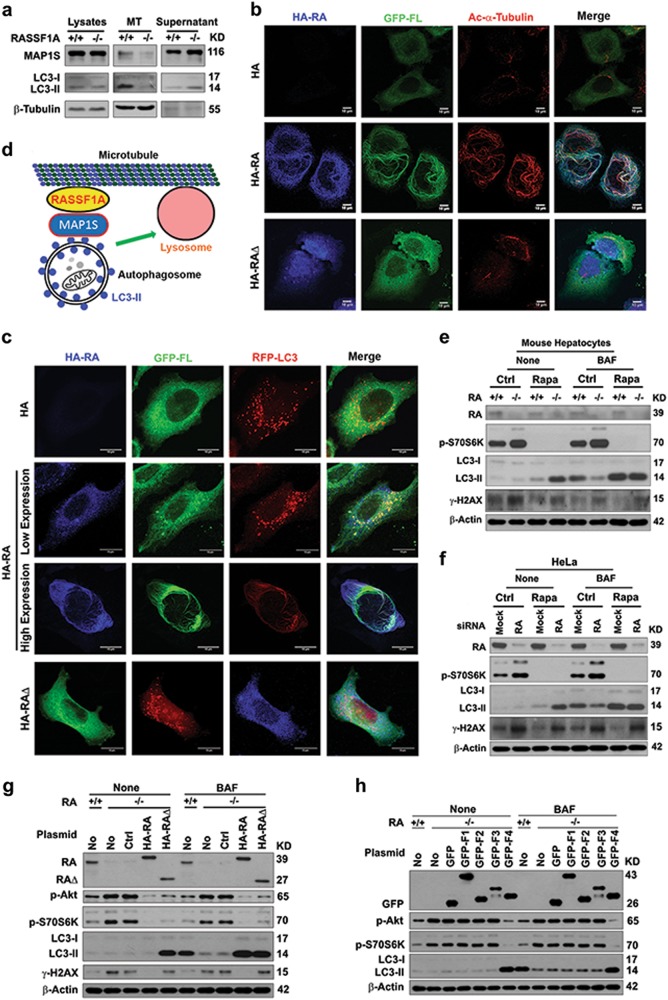
Fig. 8.
RASSF1A helps recruit autophagosomes onto acetylated microtubules through MAP1S and regulates autophagy initiation and autophagosomal degradation. a Representative immunoblots showing levels of MAP1S and LC3 associated with microtubules assembled in vitro. MT, assembled microtubules. β-Tubulin serves as the marker for assembled microtubules. b, c Representative fluorescent images showing the impact of RASSF1A (blue) on the distribution of GFP-FL MAP1S (green) and acetylated α-tubulin (red) (b) or RFP-LC3 (red) (c) in HeLa cells transiently expressing HA-tagged RASSF1A and GFP-tagged FL (b) or HA-tagged RASSF1A, GFP-tagged FL and RFP-LC3 (c). d A diagram showing the mechanism by which RASSF1A promotes autophagosomal trafficking. e, f Representative immunoblots showing the levels of p-S70S6K, LC3, and γ-H2AX in hepatocytes isolated from wild-type and RASSF1A−/− mice (e) or HeLa cells treated with random (Mock) and RASSF1A-specific siRNAs (RA) (f) untreated (Ctrl) or treated with rapamycin (Rapa) in the absence (None) or presence of bafilomycin A1 (BAF). g Representative immunoblots showing the levels of p-Akt, p-S70S6K, LC3, and γ-H2AX in wild-type HeLa cells (+/+) or HeLa cells with RASSF1A knockout (−/−) transiently transfected with no plasmid (No), control vector (Ctrl), HA-RA or HA-RA∆ in the absence (None) or presence of bafilomycin A1 (BAF). h Representative immunoblots showing the levels of p-Akt, p-S70S6K and LC3 in wild-type HeLa cells (+/+) or HeLa cells with RASSF1A knockout (−/−) transiently transfected with no plasmid (No), control vector (GFP), GFP fused fragments in the absence (None) or presence of bafilomycin A1 (BAF)