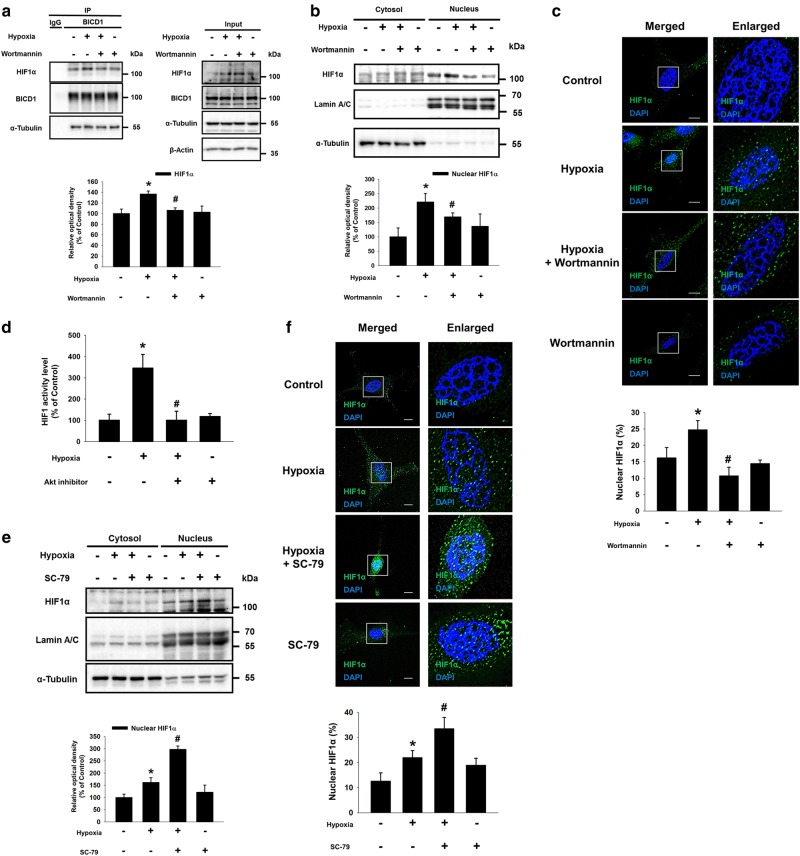
Fig. 3.
Role of hypoxia-activated Akt in BICD1-mediated HIF1α nuclear translocation. a–c The UCB-MSCs were pretreated with wortmannin (1 μM) for 30 min prior to hypoxia treatment for 24 h. a Co-immunoprecipitation of HIF1α and α-Tubulin with IgG and BICD1 antibodies were shown in left panel. Total protein expressions in lysate were shown in right panel. n = 3. b HIF1α, Lamin A/C, and α-Tubulin in cytosolic and nuclear fractionized samples were detected by western blot. n = 3. c Cells were immunostained with HIF1α-specific antibodies. Scale bars are 8 μm (Magnification, × 1,000). n = 4. d–f Cells were pretreated with Akt inhibitor (2 μM) or SC-79 (5 μg/mL) for 30 min prior to hypoxia treatment for 24 h. d HIF1 activities of UCB-MSCs were measured by dual luciferase reporter assay. n = 8. e HIF1α, Lamin A/C, and α-Tubulin protein levels in cytosolic and nuclear fractionized samples were analyzed by western blot. n = 3. f Cells were immunostained with HIF1α-specific antibody. Scale bars are 8 μm (Magnification, × 1,000). n = 4. Quantitative data are presented as a mean ± S.E.M. All blots and immunofluorescence images are representative. *p < 0.05 vs. normoxia control, #p < 0.05 vs. hypoxia