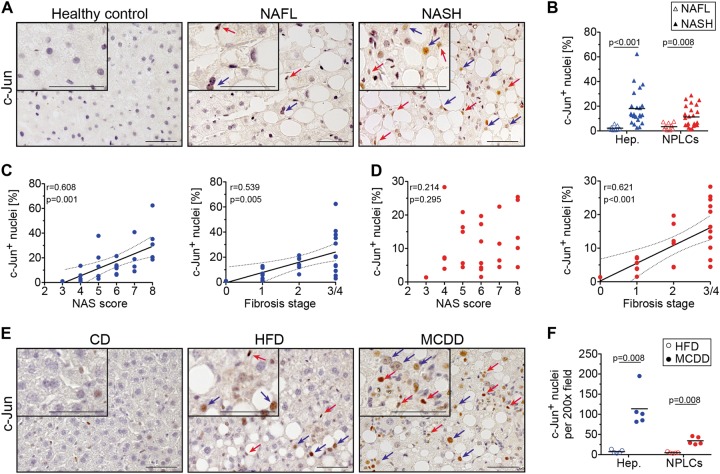
Fig. 1.
c-Jun expression correlates with disease progression from NAFL to NASH in humans and mice. a Representative immunohistochemistry for c-Jun of human liver biopsies from healthy controls, patients with NAFL or NASH. b c-Jun expression in hepatocytes and NPLCs of NAFL (n = 9) and NASH patients (n = 27) was quantified. c Hepatocellular c-Jun expression was correlated with the NAS (c, left panel) and fibrosis stage (c, right panel). d c-Jun expression in NPLCs was correlated with the NAS (d, left panel) and fibrosis stage (d, right panel). e Representative immunohistochemistry for c-Jun of livers from mice treated with a CD, HFD or MCDD. f c-Jun expression in hepatocytes and NPLCs of HFD- (n = 4) and MCDD-fed mice (n = 5) was quantified. Significance was tested by Mann–Whitney test and correlation was tested by Pearson correlation coefficient. p values are indicated if significant. Scale bar = 50 µm. Hepatocytes and NPLCs are depicted by blue and red arrows, respectively