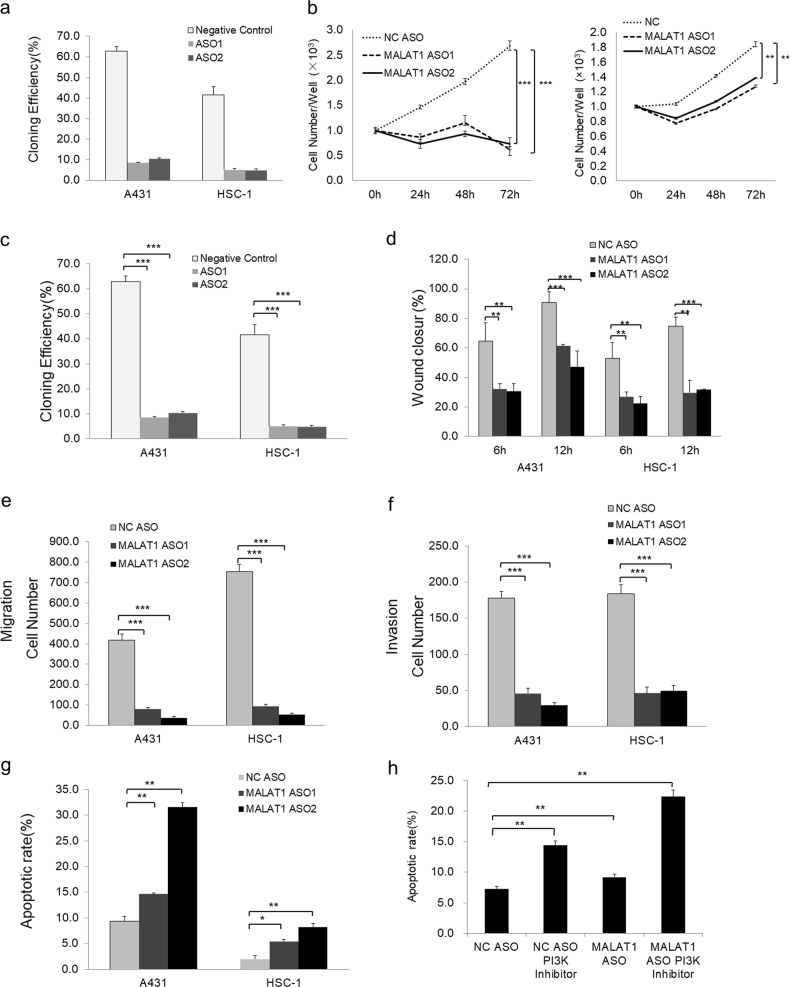
Fig. 2.
Knockdown of MALAT1 inhibits cell proliferation, mobility, migration, and invasion but promotes apoptosis of both A431 and HSC-1 cells. a Knockdown of MALAT1 in A431 and HSC-1 cells by MALAT1 ASO1 and MALAT1 ASO2 was determined by qRT-PCR assay. b CCK-8 assay determination of A431 and HSC-1 cell proliferation in response to MALAT1 knockdown. c Monolayer colony formation assay showing that MALAT1 knockdown significantly decreased the colony formation capacity of A431 and HSC-1 cells. The colony numbers were counted and recorded. d Wound-healing assay showing that knockdown of MALAT1 significantly decreased the wound closure ability of A431 and HSC-1 cells at both 6 and 12 h. e Transwell assay indicated that MALAT1 knockdown suppressed A431 and HSC-1 cell motility. f Matrigel invasion assay indicated that MALAT1 knockdown drastically inhibited A431 and HSC-1 cell invasiveness. g Flow cytometric analysis using Annexin V/PI staining showing that MALAT1 silencing significantly increased the apoptosis of A431 and HSC-1 cells (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 with LSD test of one-way ANOVA). h PI3K inhibitor LY294002 treatment led to much high apoptotic rate in addition to MALAT1 depletion-induced apoptosis. All statistical data represent the average of three independent experiments ± s.d. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001