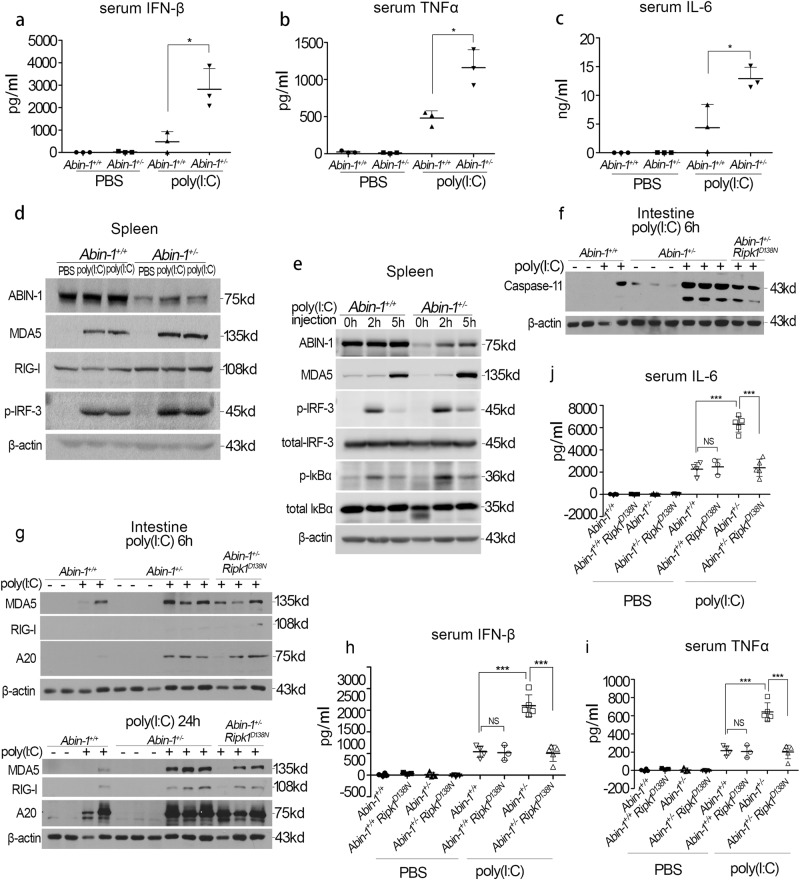
Fig. 6.
ABIN-1 deficiency enhances the poly(I:C)-induced antiviral responses in vivo. a–c ELISA analysis of serum IFN-β (a), TNF-α (b), and IL-6 (c). Abin-1+/+ and Abin-1+/− mice were i.p. injected with 5 mg/kg body weight poly(I:C) and sacrificed 1 h later. n = 3. d RIG-I, MDA5, p-IRF-3, and ABIN-1 expression in the spleen of Abin-1+/+ and Abin-1+/− mice i.p. injected with PBS or poly(I:C) (5 mg/kg body weight). Mice were sacrificed 3.5 h after drugs' injection, and the spleens were homogenized using RIPA buffer and subjected for western blot analysis. e MDA5, p-IRF-3, total IRF-3, p-IκBα, total IκBα, and ABIN-1 expression in the spleen of Abin-1+/+ and Abin-1+/− mice i.p. injected with PBS or poly(I:C) (5 mg/kg body weight). Mice were sacrificed 2 and 5 h after drugs' injection, and the spleens were homogenized using RIPA buffer and subjected for western blot analysis. f Caspase-11 expression in the small intestine of Abin-1+/+, Abin-1+/−, and Abin-1+/− Ripk1D138N mice i.p. injected with PBS or poly(I:C) (5 mg/kg body weight). Mice were sacrificed 6 h after drugs' injection, and the small intestines were homogenized using RIPA buffer and subjected for western blot analysis. g RIG-I, MDA5, and A20 expression in the small intestine of Abin-1+/+, Abin-1+/−, and Abin-1+/− Ripk1D138N mice i.p. injected with PBS or poly(I:C) (5 mg/kg body weight). Mice were sacrificed either 6 or 24 h after drugs' injection, and the small intestines were homogenized using RIPA buffer and subjected for western blot analysis. h–j ELISA assay of serum IFN-β (h), TNF-α (i), and IL-6 (j). Abin-1+/+, Abin-1+/− Ripk1D138N, Abin-1+/−, and Abin-1+/− Ripk1D138N mice were i.p. injected with 5 mg/kg body weight poly(I:C) and sacrificed 6 h later. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. from at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, NS no significant difference