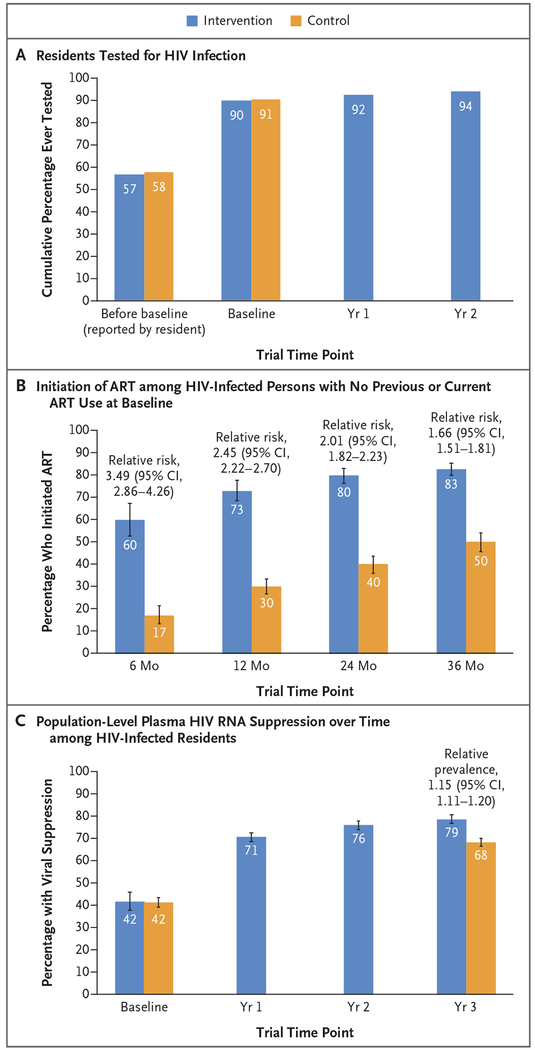
Figure 2. HIV Testing, Uptake of Treatment, and Viral Suppression.
Panel A shows the cumulative percentage of residents who underwent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) testing before and during the trial. The values labeled as “before baseline” are the percentages of the 138,052 residents (72,978 in the intervention group and 65,074 in the control group) who reported at the time of baseline testing that they had undergone previous HIV testing. The remaining values in Panel A are the percentages of all residents at the time of annual testing (excluding persons who migrated out of the community and persons who died and including persons who were newly 15 years of age and persons who migrated into the community, identified through the second census that was conducted at year 3) who had at least one documented HIV test result. At baseline, the assessment included 79,818 residents in the intervention group and 70,577 residents in the control group; at year 1, the assessment included 89,994 residents in the intervention group, and at year 2, the assessment included 93,008 residents in the intervention group. Panel B shows the percentage of persons who initiated antiretroviral therapy (ART) among HIV-infected persons with no previous or current ART use at baseline. The assessment included 3002 residents in the intervention group and 2950 residents in the control group. Community-level estimates of the probability of initiating ART by 6, 12, 24, and 36 months were calculated by the Kaplan–Meier method; data from patients who died or who migrated out of the community were censored at the time of death or out-migration. The trial groups were compared with the use of community-level targeted maximum likelihood estimation. Panel C shows population-level plasma HIV RNA suppression over time among HIV-infected residents. The assessment included all residents at the time of annual testing (excluding persons who migrated out of the community and persons who died, but including residents who were newly 15 years of age and those who migrated into the community, identified through the second census that was conducted at year 3). HIV RNA suppression was assessed in 5347 residents in the intervention group and in 4192 residents in the control group at baseline; in 6269 residents in the intervention group at year 1; in 6348 residents in the intervention group at year 2; and in 6800 residents in the intervention group and 6051 residents in the control group at year 3. Community-level estimates of suppression were adjusted for incomplete measures of HIV serostatus and HIV RNA with the use of individual-level targeted maximum likelihood estimation (adjustment variables included sex, age group, marital status, educational level, occupation, alcohol use, household wealth, mobility, previous HIV testing, and care status). The estimated total number of HIV-positive persons was 15,399 at baseline and was 15,748 at year 3. The trial groups were compared with the use of community-level targeted maximum likelihood estimation. I bars in Panels B and C indicate 95% confidence intervals.