Figure 1.
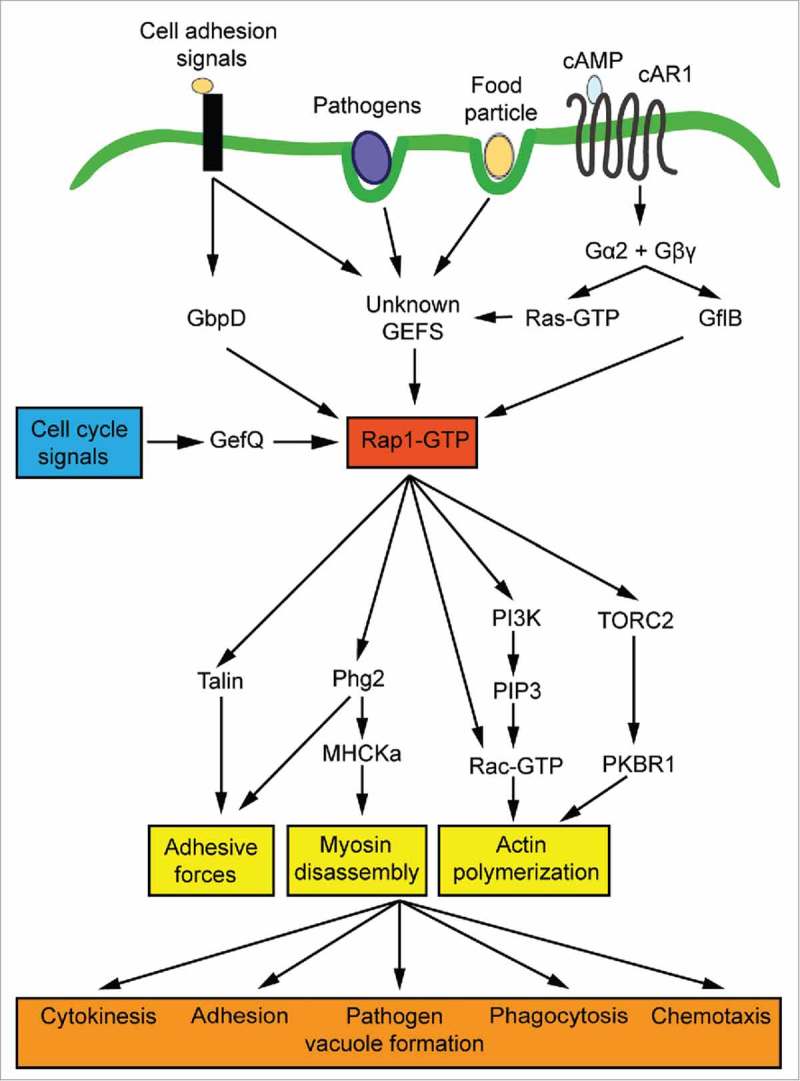
Role of the small GTPase Rap1 in signal transduction, cell dynamics and bacterial infection. Rap1 is activated in response to various extracellular and intracellular stimuli. During substrate attachment and cytokinesis, Rap1 is primarily activated by the GEFs GbpD and GefQ, respectively. In the course of chemotaxis, the Gα2-stimulated RapGEF GflB determines the balance between Rap1 and Ras activation at the leading edge of Dictyostelium cells. Other GEFs transducing the signals to Rap1 remain to be identified. Activated Rap1 is a major regulator of cytoskeletal dynamics and stimulates cellular adhesion, actin filament formation and myosin disassembly via the indicated pathways. Together, these cytoskeleton rearrangements are key for cytokinesis, adhesion, pathogen vacuole formation, phagocytosis and chemotaxis.
