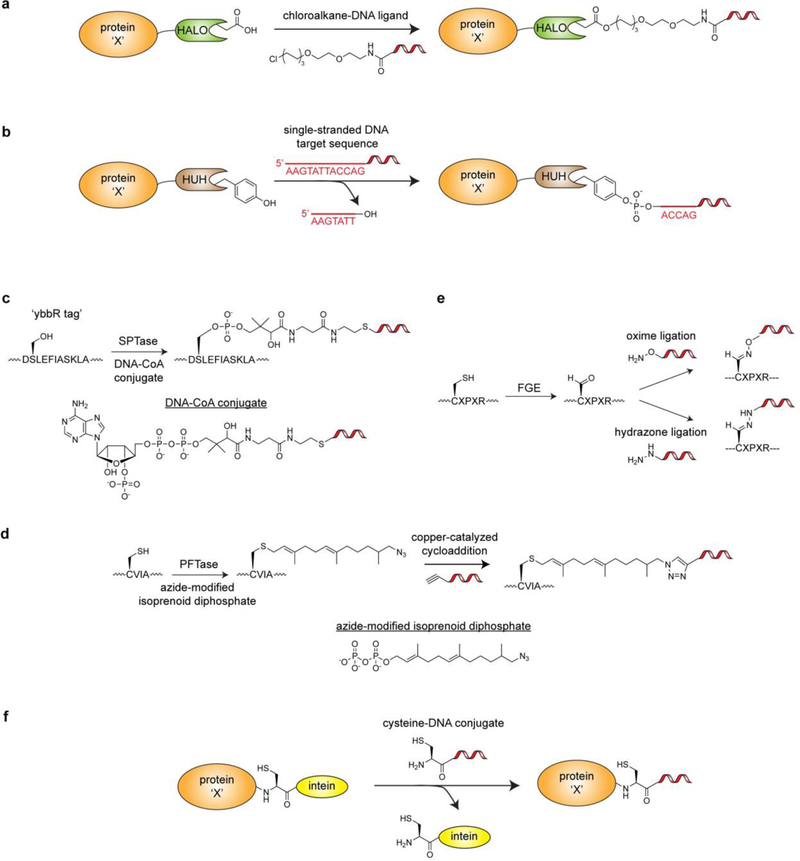
Figure 11.
Genetically encodable fusion tags that enable bioorthogonal labeling of proteins with DNA. a) Labeling of a protein-HALO tag fusion with a chloroalkane-DNA conjugate. b) Labeling of a protein-HUH domain fusion with a single stranded DNA fragment via a stable 5’-phosphotyrosine linkage. c) Sfp phosphopantetheinyl transferase (SPTase)-mediated labeling of the ybbR tag via a DNA-CoA conjugate. d) Protein farnesyltransferase (PFTase)-mediated labeling of the CVIA motif with an azide-modified isoprenoid diphosphate substrate. A subsequent copper-catalyzed cycloaddition reaction can be used to append an alkyne-functionalized DNA strand. e.) Formylglycine Generating Enzyme (FGE)-mediated labeling of the CXPXR motif. FGE is used to generate an aldehyde handle that can be used in subsequent oxime and hydrazone ligations with appropriately functionalized DNA strands. f) Labeling of a protein-intein fusion with a cysteine-DNA conjugate.