Figure 5.
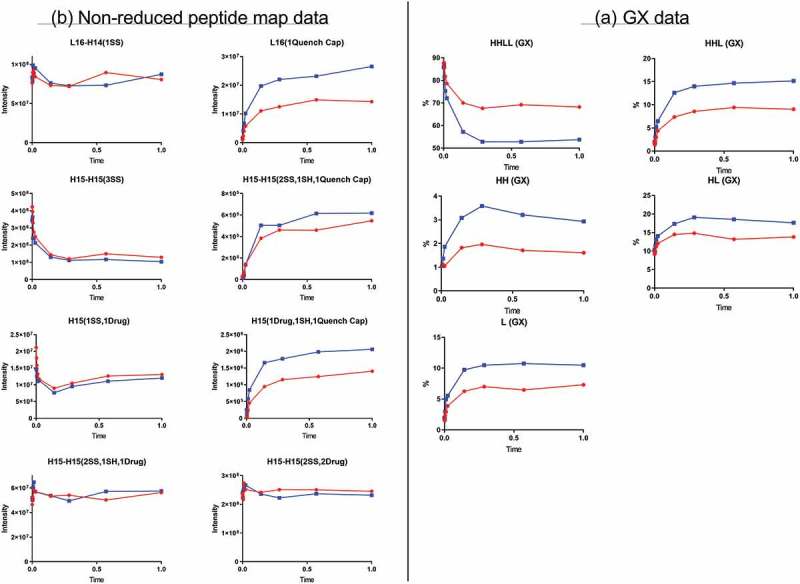
Quench time-course data. Red and blue represent two different quench conditions. (A) GX data. H, heavy chain; L, light chain; HL, combination of heavy chain-light chain; HH, combination of heavy chain-heavy chain; HHL, combination of heavy chain-heavy chain-light chain; HHLL, heavy chain-heavy chain-light chain-light chain. (B) Nonreduced peptide map data. H15 is the hinge peptide containing three cysteines: two that form interchain disulfide bonds between the two heavy chains, and another engineered cysteine designed for conjugation. H14 and L16 are peptides containing cysteines that connect the heavy chain and light chain. H15-H15 (2SS, 2Drug) is the desired product from the conjugation reaction. L16-H14 (1SS), peptide containing a disulfide bond between the light chain and heavy chain; L16 (1 Quench Cap), L16 attached to a molecule of quenching reagent; H15-H15 (3SS), triple-disulfide bond peptide structure (unconjugated antibody); H15-H15 (2SS, 1SH, 1Quench Cap), triple-disulfide bond structure with a molecule of quenching reagent attached; H15 (1SS, 1Drug), half-ADC; H15 (1Drug, 1SH, 1Quench Cap), half-ADC with a molecule of quenching reagent attached; H15-H15 (2SS, 1SH, 1Drug), underconjugated ADC.
