Figure 1: Sdk localizes to tAJs.
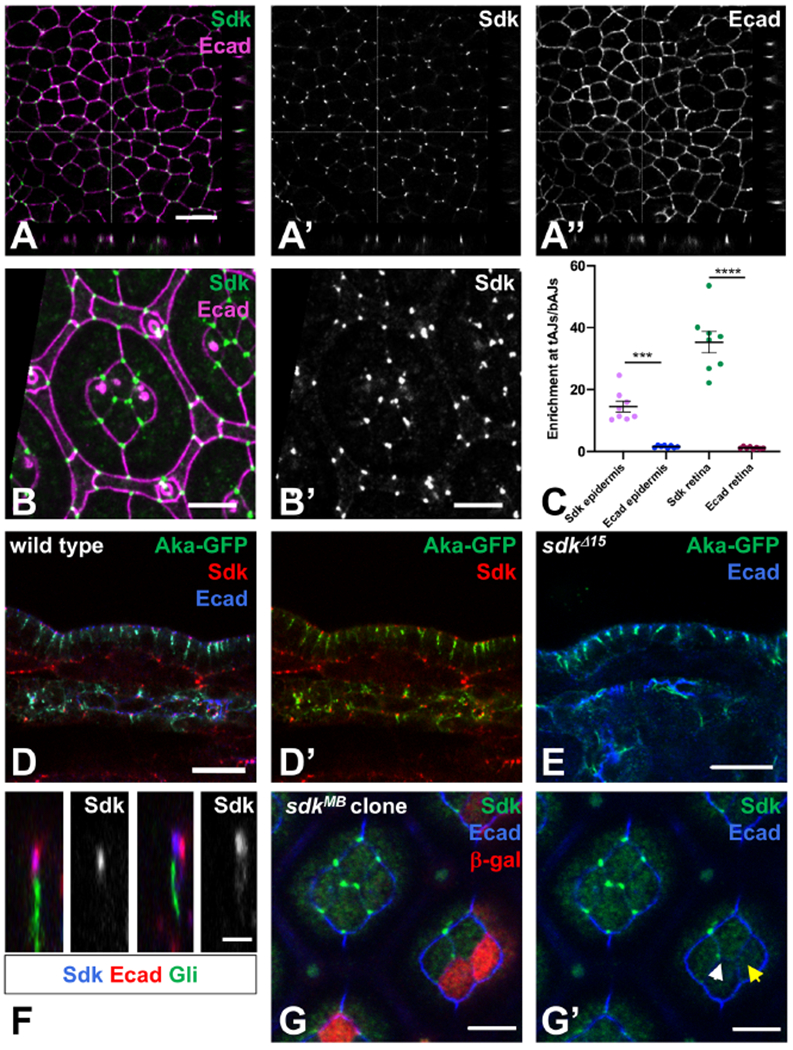
(A) Single confocal section of a wild type stage 10 embryo stained for Sdk (A’, green) and Ecad (A’’, magenta) showing the apical surface of the epidermis and xz and yz sections. (B) Apical surface of a 42 h pupal retina, stained for Ecad (magenta) and Sdk (B’, green). Four central cone cells are surrounded by two primary pigment cells and a lattice of secondary and tertiary pigment cells and mechanosensory bristles. (C) Quantification of Sdk and Ecad enrichment at tAJs relative to adjacent bAJs in stage 9-11 embryonic epidermis and in cone cells in 42h pupal retina. n=8 samples of each tissue, with each point being the mean of 10 cells from that sample. Bars show mean ± SEM. ****, p<0.0001, ***, p=0.0001, unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. (D, E) cross-sections of the epidermis and the dorsal tracheal trunk of wild type (D) and sdkΔ15 (E) stage 15 embryos, stained for Sdk (red), Ecad (blue) and Aka-GFP (green). n=18 (D), n=8 control and 14 sdk (E). (F) xz sections of wild type 42 h pupal retina stained for Sdk (blue and single channels), Ecad (red) and Gli (green). n=15. Sdk is strongly enriched at tricellular vertices, at the same apical-basal level as and usually overlapping with Ecad, and apical to Gli and Aka. Aka localization is not affected in sdk mutants. (G) a sdkMB05054 clone marked with anti-β-galactosidase in red, stained for Sdk (green) and Ecad (blue), in a focal plane at the level of cone cell apical junctions. Sdk is absent from the tAJ when two of the three cells are sdk mutant (yellow arrow in G’) but present when only one cell is mutant (white arrow). Scale bars, 10 μm (A, D, E) 5 μm (B, G), or 2 μm (F). See also Figure S1.
