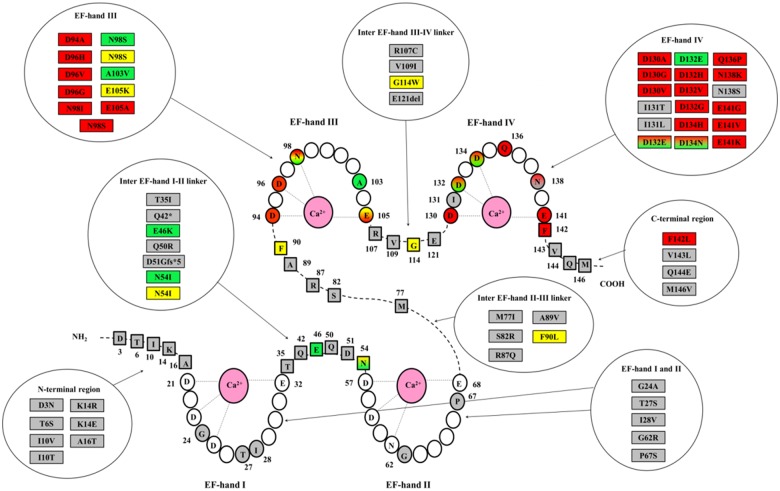
Figure 1.
Schematic model of calmodulin with the 4 Ca2+ binding loops (EF-hands I-IV) and amino acids principally involved in the binding of Ca2+ ions denoted with light grey lines. Coloured amino acid residues (circles in EF-hands and squares in linkers and N-/C-terminal regions) represent positions affected by genetic variants, identified either in patients of the Registry or in subjects of the general population (gnomAD database22). All amino acid changes so far identified are listed in circular boxes according to a colour code for the associated phenotype: red for long QT syndrome, green for catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, yellow for idiopathic ventricular fibrillation, sudden unexplained death or atypical phenotype, grey for variants identified in the gnomAD database. The corresponding amino acid positions in the protein are highlighted with the same colour code. Shaded colours stand either for overlap phenotype or for an association with multiple distinct phenotypes.