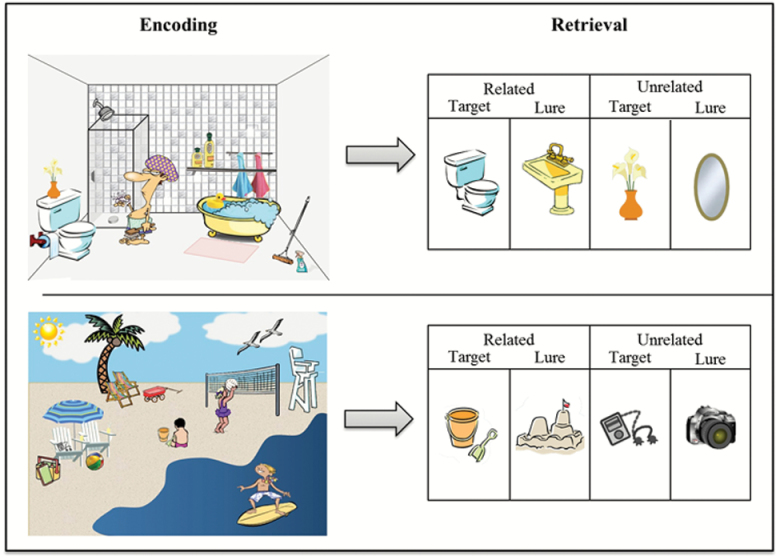
Figure 1.
Schematic scene memory paradigm. During encoding, participants viewed schematic scenes (e.g., Bathroom, Beach). During retrieval, in the MRI scanner, participants made “Remember,” “Know,” or “New” responses to both schematically related targets (e.g., toilet, sand pail/shovel) and lures (e.g., sink, sandcastle), as well as unrelated targets (e.g., flower vase, music player) and lures (e.g., mirror, camera).