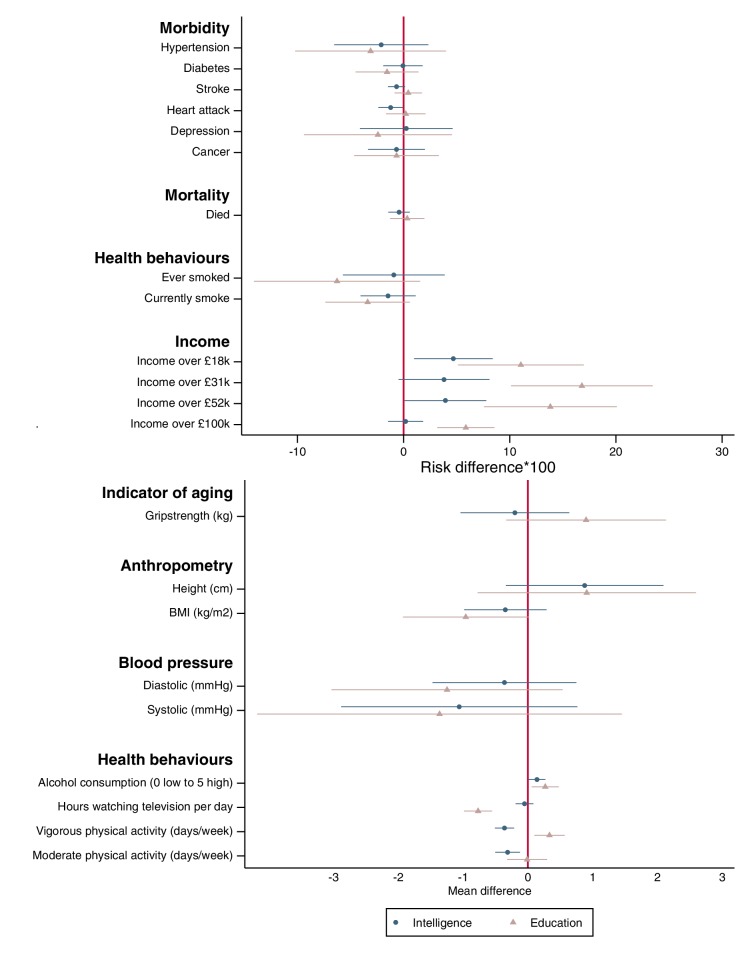
Figure 4. The direct effects of SD changes in years of education and intelligence on later outcomes in UK Biobank.
The error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals around the estimated effects. Estimated using two sample multivariable Mendelian randomization. Higher intelligence had direct effects on higher household income and alcohol consumption and less moderate and vigorous physical activity. Higher education had direct effects on decreased smoking, BMI, and sedentary behaviour and increased household income and rates of vigorous physical activity. These are estimates of the direct effects of intelligence (education) that are not mediated via education (intelligence).