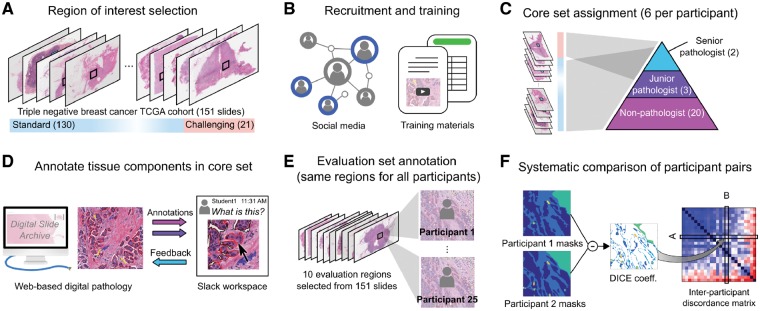
Fig. 1.
Study overview. (A) Slides from the TNBC cohort were reviewed for difficulty and the study coordinator selected a single representative ROI in each slide. (B) Participants were recruited on social media from medical student interest groups. Documentation and instructional videos were developed to train participants in breast cancer pathology and the use of DSA annotation tools. A spreadsheet lists slide-level descriptions of histologic features for each of the 151 images to aid in training. (C) Participants were each assigned six slides based on experience. Challenging slides were assigned to faculty/pathology residents, while standard slides were distributed among all participants. (D) The DSA was used by participants to draw the outlines of tissue regions in their assigned slides/ROIs. A Slack workspace enabled less experienced users to ask questions and receive guidance from the more experienced users. (E) Ten evaluation ROIs were identified in the slides and were annotated by all participants in an unsupervised manner to enable inter-participant comparisons. (F) Agreement between each pair of participants was evaluated using the Dice coefficient to generate an inter-participant discordance matrix