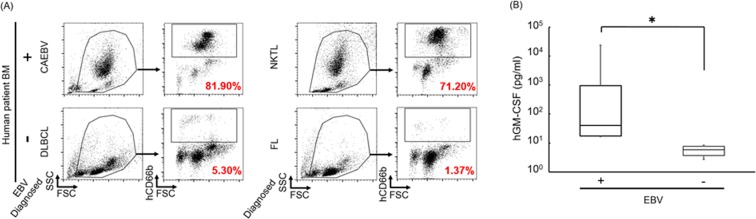
Figure 5.
Increased GM-CSF and granulopoiesis were detected in hematopoietic disorder patients with EBV infection. (A) Comparison of granulocyte population in BM between EBV-infected and uninfected patients. Anti-human CD66b Ab was used for the detection. Collected EBV+ patient’s samples were CAEBV (n = 1), NKTL (n = 2), and EBV- patient’s samples were DLBCL (n = 1), FL (n = 2) patients, respectively. Formal name of each abbreviations is bellow; CAEBV = Chronic active EBV infection, NKTL = NK/T-cell lymphoma, DLBCL = Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, FL = Follicular lymphoma. Representative data are indicated. (B) ELISA assay of hGM-CSF in serum of patients. EBV+ data were detected from HLH (N = 8) and PTLD (N = 4) patients, EBV− data were detected from sJIA (N = 2) and KD (N = 4) patients. Data are mean ± SD. Significant difference was detected between EBV infected patients and uninfected patients. HLH = Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, PTLD = post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder, sJIA = systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, KD = Kawasaki disease. *p < 0.05.