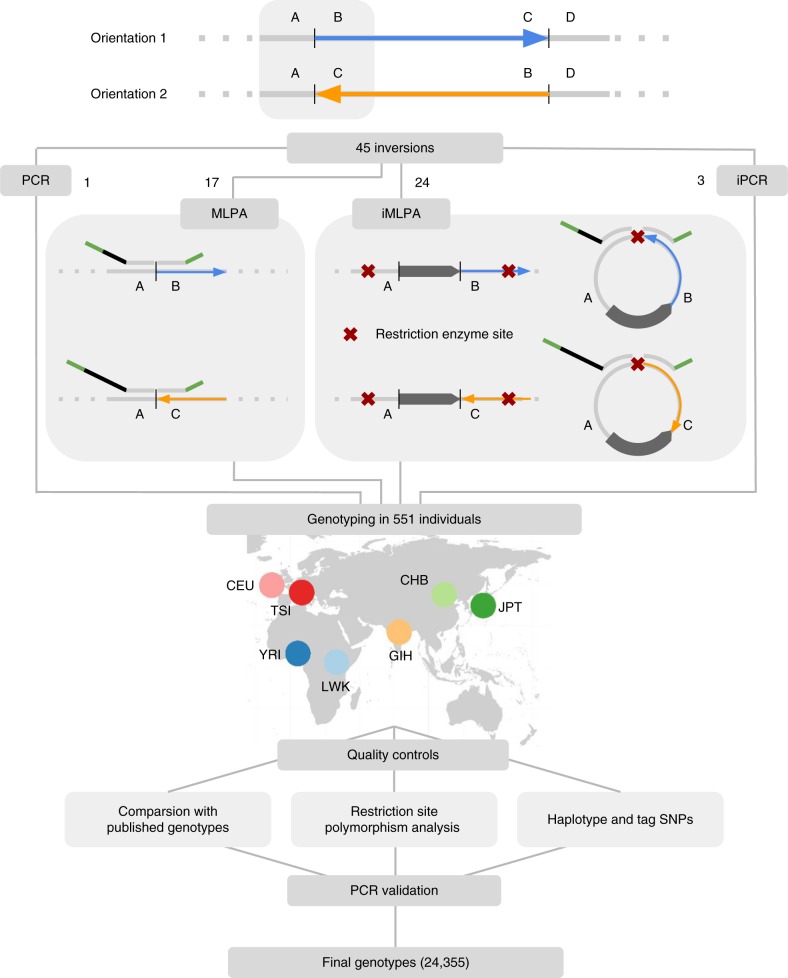
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of inversion genotyping strategy. High-throughput genotyping of the 45 inversions in 551 individuals from different populations was done by MLPA (17), iMLPA (24), regular PCR (1) and iPCR (3). To avoid confusion about the ancestral status, the two inversion orientations have been named as 1 (AB and CD breakpoints) and 2 (AC and BD breakpoints), using the hg18 genome assembly as reference (Supplementary Data 1). In MLPA and iMLPA, two pairs of oligonucleotide probes (represented in top of the genome sequence) that are able to hybridize contiguously to the target region through a specific sequence complementary to the genome (light grey) were used to interrogate the two alternative orientations of each inversion. These probes, which include a stuffer sequence of variable length (black), are ligated together in a subsequent step and the resulting products are amplified for all the analyzed inversions at the same time with common primers (in green). IRs or other repetitive sequences at the breakpoints are represented as a dark pointed rectangle