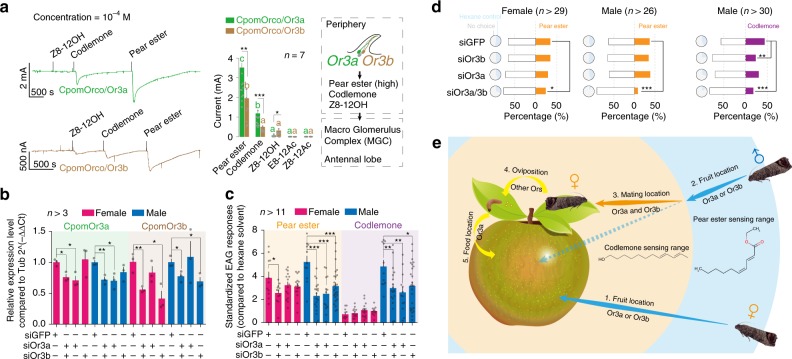
Fig. 4.
Functional demonstration of CpomOR3a/CpomOR3b in pear ester and codlemone olfactory reception of the codling moth, Cydia pomonella. a Comparison of CpomOR3a and CpomOR3b responses to different chemical components with Xenopus expression system. Example traces of CpomOR3a/CpomORco and CpomOR3b/CpomORco injected Xenopus oocytes are shown respectively, with current elicited by Z8-12OH, codlemone, and pear ester solutions at 10−4 M concentration. Lower case letters indicate significant differences (ANOVA and Tukey HSD, F4, 45 = 161.8, P < 0.0001), or CpomOR3b/CpomORco injected oocytes (ANOVA and Tukey HSD, F4, 45 = 22.3, P < 0.0001). * indicates significant differences (Student’s t test, pear ester: t15 = 3.6, P = 0.0027; codlemone: t15 = 4.2, P = 0.0008; Z8-12OH: t17 = 2.5, P = 0.0235). Error bars indicate + SEM. (b) Quantitative PCR tests for RNAi strains. Data were calculated based on the 2−ΔΔCt method with normalization to Cpomβ-tubulin. * indicates significant influences (Student’s t test, CpomOR3a, female, siOR3a/b: P = 0.0118, siOR3a: P = 0.0181; male, siOR3a/b: P = 0.0019, siOR3a: P = 0.0273 (one-tail); CpomOR3b, female, siOR3a/b: P = 0.0090, siOR3b: P = 0.0171; male, siOR3a/b: P = 0.0284, siOR3b: P = 0.0035). Error bars indicate + SEM. c Electroantennogram (EAG) results with RNAi strains to pear ester and codlemone. * indicates significant decrease (Student’s t test, pear ester, female, siOR3a/siOR3b: t21 = 2.4, P = 0.028; pear ester, male, siOR3a/siOR3b: t28 = 5.3, P < 0.0001, siOR3a: t22 = 4.1, P = 0.0004, siOR3b: t35 = 3.7, P = 0.0007; codlemone, male, siOR3a/siOR3b: t28 = 2.8, P = 0.009, siOR3a: t22 = 3.1, P = 0.005, siOR3b: t35 = 2.5, P = 0.018). Error bars indicate + SEM. d Y-tube assays of RNAi strains. Distributions of counts among choosing of tested chemicals, hexane, and no choice were compared between each injected strain with siGFP strain by chi-square test. Bar charts indicate proportions of counts between positive choice (either codlemone or pear ester) and negative (no choice and hexane control). * indicates significant differences between current treatment with siGFP strain (pear ester, female, siOR3a/siOR3b: χ = 9.5, P = 0.0084; pear ester, male, siOR3a/siOR3b: chi = 24.4, P < 0.0001; codlemone, male, siOR3a/siOR3b: χ = 47.4, P < 0.0001, siOR3b: χ = 10.5, P = 0.0053). e Schematic illustration showing predicted OR3a and OR3b mediated behaviors in C. pomonella. Step 1: female adults locate fruits and find mating sites on leaves. Step 2: male adults locate fruits as potential mating sites from a long distance. Step 3: male adults locate females in a close distance via codlemone sensing process. Steps 4 and 5: oviposition of females and food location of newly hatched larvae via OR3a detection of pear ester. Source data are provided as a Source Data file