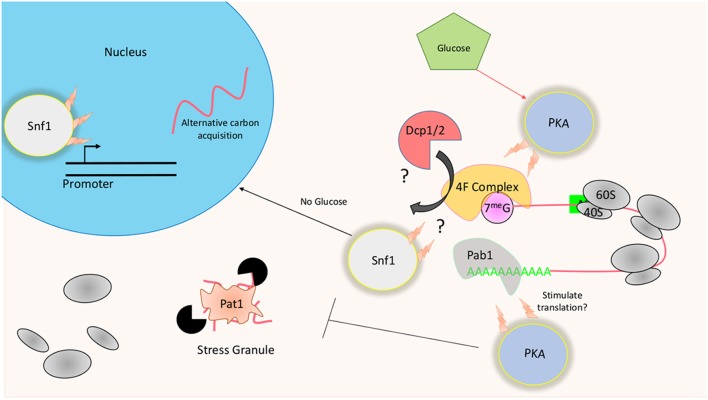
Figure 3.
Translational regulation in response to glucose availability: The presence of glucose results in the activation of PKA promoting high levels of protein biogenesis. At the translational level, this may be achieved through the phosphorylation of Dcp1/2 or Pat1. Phosphorylation of the decapping enzymes may weaken interactions with the 5′ cap, instead allowing the translational machinery to associate with the mRNA. PKA may also act to stimulate translation through post-translational modifications of Pab1. Snf1 kinase is known to promote the transcription of the alternative carbon utilization pathway. Long term effects of its deletion may promote a proteome that is already preadapted to glucose mediated translational suppression.