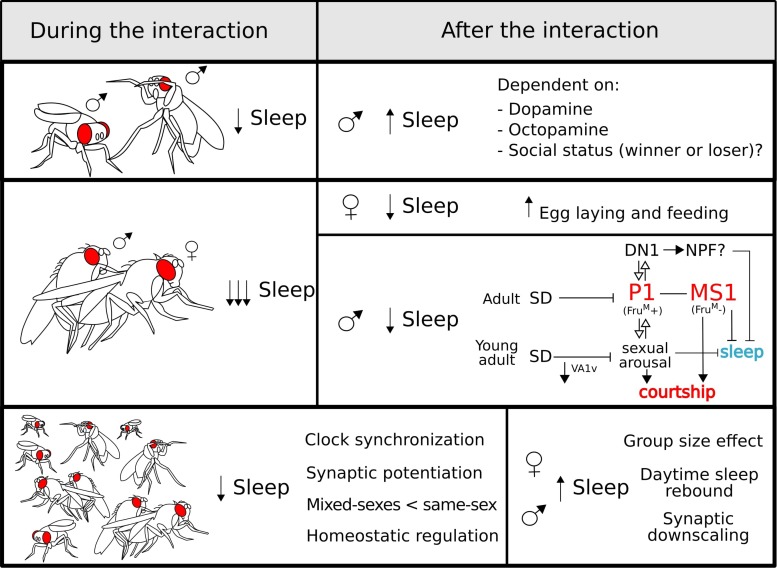
FIGURE 3.
Sleep regulation during (left panel) and after (right panel) different social interactions: sexual (top), aggressive (middle), and group (bottom). During all the interactions, sleep is reduced which is most poignant for sexual encounters. After copulation, males undergo a negative regulation of sleep controlled by sex-drive-related neurons (see the main text for a detailed explanation). For the group interaction (bottom panel), some characteristics of this type of interaction are highlighted. After a social encounter, the effects on sleep regulation vary depending on the type of interaction and the sex of the fly.