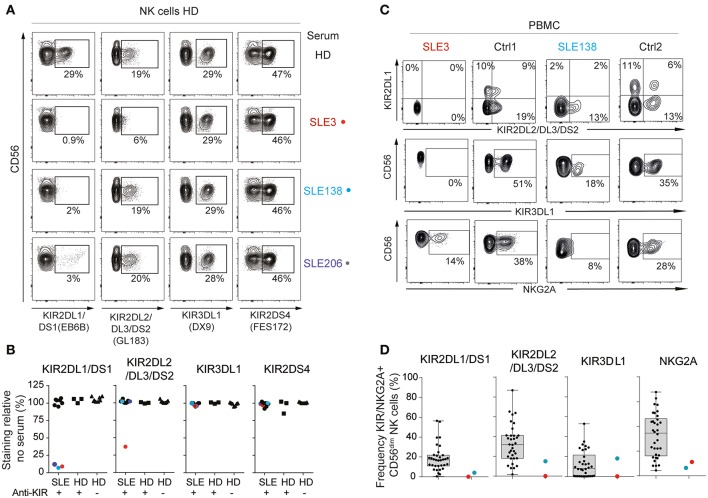
Figure 2.
Anti-KIR autoantibodies from SLE patients block the binding of monoclonal anti-KIR antibodies. (A,B) Flow-cytometric KIR stainings of healthy donor (HD) cells following 30 min incubation with 50% serum from patients harboring >3 anti-KIRs (n = 10), KIR-positive HD (n = 3), and KIR-negative (n = 8) HD (A) Flow cytometry plots from one representative HD and the three SLE patients that blocked the binding of anti-KIR2DL1/DS1. (B) The frequency of KIR-positive cells in serum-treated cells relative to the mean frequency of KIR-positive cells in eight non-treated cells. (C,D) Flow-cytometric KIR stainings of CD3−CD56dim NK cells in PBMCs from anti-KIR-negative (n = 34), and anti-KIR-positive SLE patients (n = 2). Data are from two separate experiments. (C) Flow cytometry plots from SLE3, SLE138 and one representative HD from each experiment. (D) Data for all patients presented as boxplots, with the median, interquartile range, and range denoted.