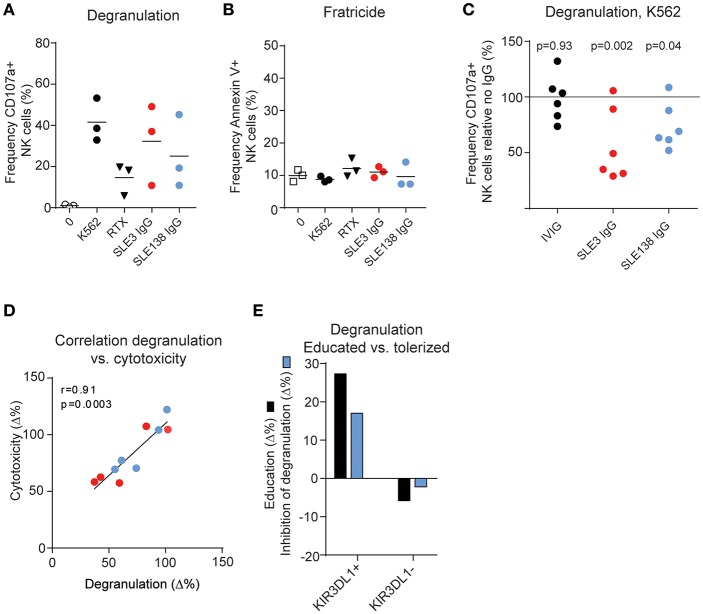
Figure 3.
Anti-KIR autoantibodies induce hyporesponsiveness in NK cells. (A) NK cell degranulation and (B) viability of IL-2-activated PBMCs from 3 HDs following incubation with K562 cells, rituximab (RTX, anti-CD20), or IgG as indicated. (C) K562-induced degranulation in NK cells from 6 HDs exposed to IgG from patient SLE3, SLE138, or HDs (IVIG) relative to no IgG. P-values from a repeated measures one-way ANOVA comparing the relative degranulation in IgG-treated cells to untreated cells are shown. (D) Correlation between the difference in degranulation and the difference in cytotoxicity of IgG-treated NK cells compared to non-treated NK cells. (E) Comparison of the education level and the inhibitory effect of SLE138-IgG on degranulation compared to no IgG. Education level was defined as the difference in degranulation in indicated NK cell subsets relative to KIR-negative NK cells (KIR2DL1/DS1−KIR2DL2/DL3/DS2−KIR3DL1/DS1−) in the absence of IgG. (A–E) Data from patient SLE3 and SLE138 are colored in red and blue, respectively.