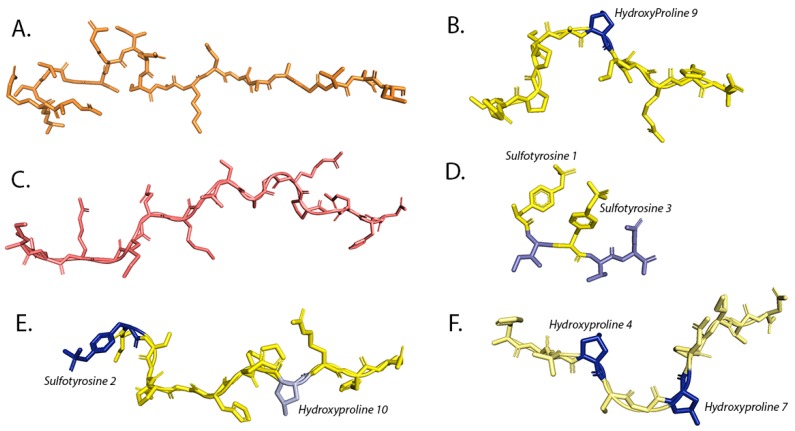
Figure 1.
Structures of small secreted peptides ligands of LRR-RLKs in stick representation: flg22, Inflorescence Deficient in Abscission (IDA), PEP1, phytosulfokine (PSK), RGF1, and tracheary element differentiation inhibitory factor (TDIF). (A) flg22 (colored in orange) is the epitope of bacterial flagellin that can elicit immune response after interacting with FLS2 ectodomain (PDB ID 4MNA). (B) IDA (colored in yellow) interacts with HAESA LRR ectodomain (PDB ID: 5IXQ). IDA contains a hydroxyproline residue at the ninth position (colored in blue) (C) PEP1 peptide (colored in salmon) is responsible for generating immune response in the plant by inducing heterodimerization of PEPR1 (PDB ID 5GR8) and its co-receptor BAK1. (D) PSK is a five amino acid long hormone (colored in cyan) that contains two sulfo-tyrosine residues (colored in yellow). These two sulfate moieties directly interact with the PSKR LRR (PDB ID: 4Z63). (E) RGF1 peptide (colored in yellow) is involved in maintaining stem cell niche in root and is perceived by the RGFR1 receptor. (PDB ID 5HYX). RGF1 peptide contains two post-translationally modified residues; sulfated tyrosine (colored in blue) and hydroxyproline (colored in cyan). (F) TDIF is a dodecapeptide (colored in pale yellow) which is perceived by the TDR receptor (PDB ID 5JFI). TDIF inhibits xylem cell differentiation and promotes procambial cell proliferation. It contains two hydroxyproline residues in fourth and seventh position (colored in blue).