Figure 1.
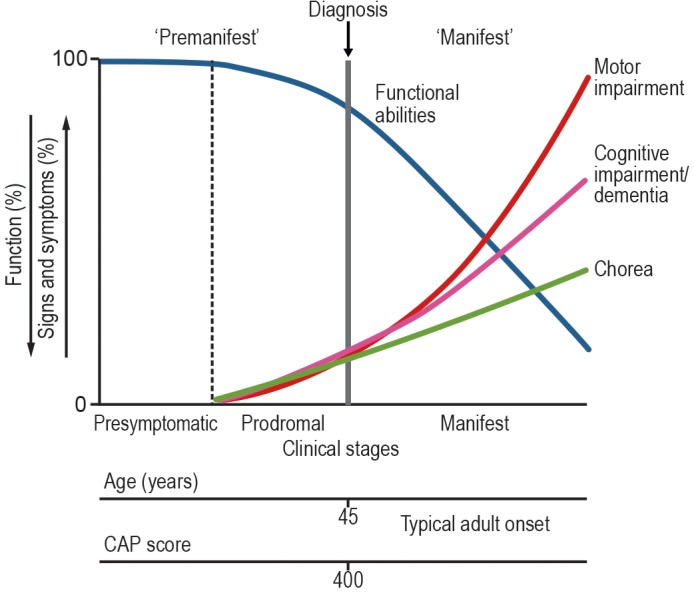
Diagnostic categories defined in this paper in the context of Huntington's disease (HD) natural history. The Cytosine, Adenine, Guanine (CAG) expansion in the Huntingtin gene is present at birth, and the mRNA and protein are widely expressed during development and adulthood, so the biological processes underlying the clinical syndrome are continuously active during the individual's lifetime. The extent of exposure to the effects of the CAG expansion can be quantified using the CAG age product (CAP) score (see text). The “premanifest HD” period before diagnosable onset according to the criteria proposed includes both the “presymptomatic HD” period, when there are no detectable clinical features, and the prodromal HD period, when there are subtle changes in motor and cognitive (and often emotional) function, with consequent subtle changes in functional abilities. During the manifest HD period, the motor and cognitive features progress, and functional abilities decline.
