Figure 1.
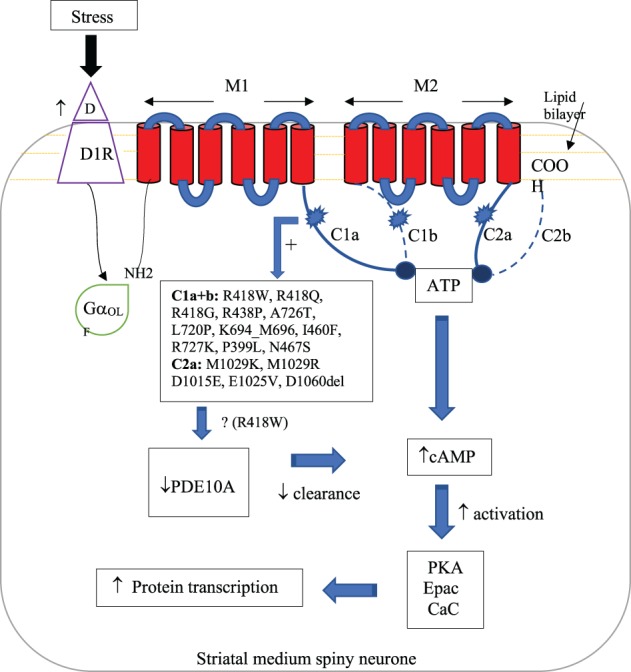
Proposed disease mechanism. Stress increases striatal dopamine synthesis and release, heightening receptor sensitivity while activating ADCY5 through GαOLF. ADCY5 mutations result in a gain‐of‐function response to this stimulus with increased binding of ATP by the catalytic pocket (C1a and C2a) as well as downstream decreased PDE10A expression. Both of these increase levels of cAMP and subsequent downstream cellular activity. Abbreviations: D, dopamine; D1R, dopamine receptor 1; GαOLF, stimulatory G protein; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; Epac, exchange proteins activated by cAMP; CaC, calcium channels; PDE10A, phosphodiesterase 10A.
