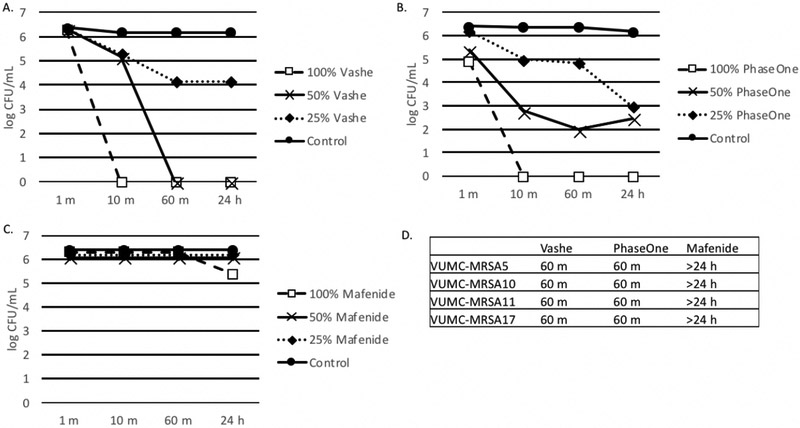
Figure 2. Effect of Wound Solutions on methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA).
A-C. Biofilms were formed in 100 μl BHI with 1% glucose. MRSA ATCC 43000 (panels A-C) or clinical strains of MRSA (panel D). Organisms were added to tissue culture treated plates and incubated for 24 h at 35°C. After 24 h biofilms were washed with 1X PBS three times and 100 μl, 50% or 25% Vashe (panel A), PhaseOne (panel B) or Mafenide (panel C) were added to the wells. Control wells contained 100 μl PBS. Plates were incubated for 1 m, 10 m, 60 m or 24 h. Wells were washed three times with PBS to remove the wound solutions and reconstituted with 100 μl H2O. Bacterial viability was monitored by the CFU assay. D. This data represents the minimum time to kill (CFU=0) clinical strains of MRSA with Vashe, PhaseOne or Mafenide. Bacteria that were not killed at 24 h are indicated by >24 h.
Panels A-D are representative of 3 independent experiments.