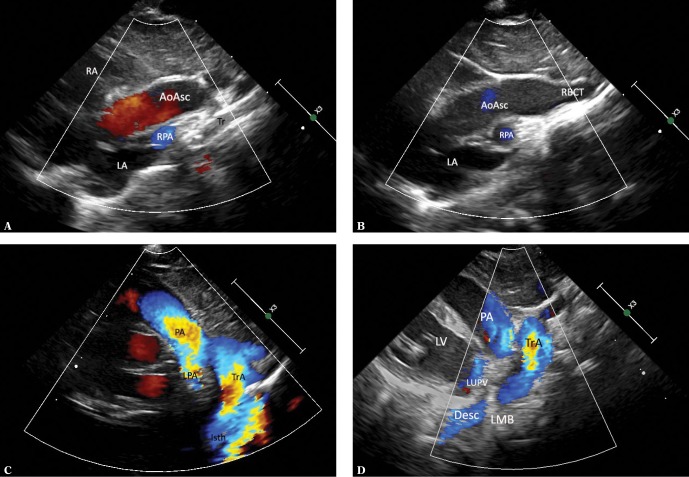
Fig. 3.
Thoracic aorta in a patient with left aortic arch in sagittal-like parasternal views. The transducer located in the left parasternal line, slightly lower than in Fig. 1A and 1B (right-to-left scan). A. Ultrasound beam directed slightly rightwards, showing the ascending aorta (AoAsc) with the bulb. The right pulmonary artery (RPA) passes immediately behind the aorta. Other visible elements: left atrium (LA), right atrium with a fragment of its appendage (RA), an esophageal and tracheal shadow (Tr). B. A slightly more medial course of the ultrasound beam visualizes the initial segment of the transverse aortic arch and the initial segment of the brachiocephalic trunk (RBCT). Other legends as in Fig. 2A. C. A slight tilt of the transducer to the left of the medial plane with minimal rotation to the left visualizes the transverse aortic arch (TrA) and the initial segment of the descending aorta – the isthmus (Isth), as well as the pulmonary artery trunk (PA) and the initial segment of its left branch (LPA), which anteriorly crosses the descending aorta. D. A further slight tilt of the ultrasound beam to the left visualizes almost the entire descending aorta (Desc), as well as the distal segment of the aortic arch (TrA), the pulmonary artery (PA), the left upper pulmonary vein (LUPV) and the left ventricle (LV). The color-coded stream in the descending aorta is apparently interrupted at the level of the upper wall of the left atrium by an acoustic shadow produced by the left main bronchus (LMB), which anteriorly crosses the aorta and is located between the transducer and the aorta. The characteristic course of the individual aortic segments, which may be followed by performing maneuvers described in Fig. 2A, B and 3 A–D, is a decisive phenomenon for the assessment of aortic arch location and course. In the case of the left aortic arch, the aorta gradually travels to the front, rightwards and backwards, posteriorly crossing the left pulmonary artery. The characteristic convexity of the arch is directed to the left and upwards. The first branch, usually a wide brachiocephalic trunk, which divides after a short course, is directed to the right. In the case of the right aortic arch, the convexity of the arch is directed to the right, while the descending aorta remains on the right side of the chest and posteriorly crosses the right pulmonary artery, and the first branch is always directed to the left