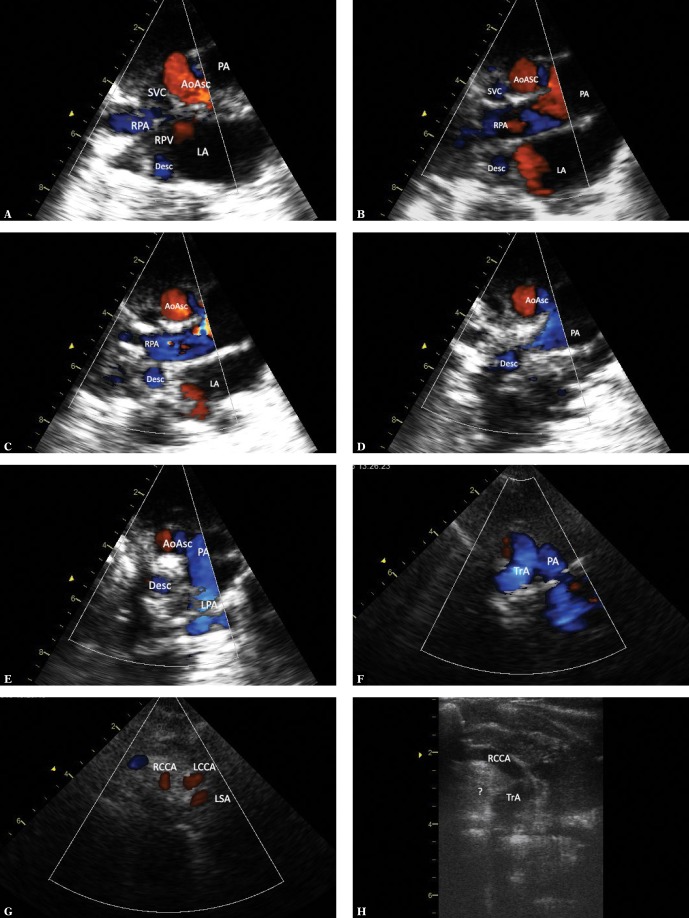
Fig. 5.
Imaging of the left aortic arch with the right descending artery. The images were obtained by gradually tilting the ultrasound beam posteriorly and upwards from the frontal plane until reaching a horizontal plane. A. Suprasternal view – frontal plane. Systolic phase. The ascending aorta (AoAsc) is seen in the centre, with the left atrium (LA) located below. The transverse section of the descending aorta (AoDesc) is seen behind the right wall of the left atrium, posteriorly from the orifice of the right pulmonary veins (RPV). Furthermore, the pulmonary artery trunk (PA) is located left to the aorta; on the right side – the superior vena cava (SVC) and a part of the right pulmonary artery (RPA). It is noteworthy that the descending aorta is located exactly posteriorly from the superior vena cava – to the right from the midline – a phenomenon typical of right aortic arch. B. Ultrasound beam shifted slightly more posteriorly and horizontally. Legends as in previous figures. At this level, the descending aorta is adjacent to the posterior wall of the right pulmonary artery and is also located exactly posteriorly from the SVC. C. A slightly more horizontal plane – legends as in previous figures. The descending aorta is slightly closer to the ascending aorta, which is now seen in a transverse section. D. Continued upward scanning – the descending aorta is located just below the right pulmonary artery and is gradually approaching the ascending artery, still on the right side of the midline. E. A nearly horizontal plane. It is only at this level that the untypically coursing left pulmonary artery (LPA) directed posteriorly instead of leftwards in its initial course is visible. Although the descending aorta is closer to the ascending aorta, it is still located on its right side. A strongly hyperechoic trachea is located between the ascending and descending aorta. F. A section at the level of aortic arch (TrA). The convexity of the aortic arch is directed to the left, which is typical of the left aortic arch. G. A cross-section at the level of arch branches. The first branch is directed rightwards, the two other branches are directed to the left. This pattern points to a left aortic arch. A similar diameter of these vessels is noticeable (the first vessel and the two other vessels have similar diameters); therefore, the presence of an aberrant right subclavian artery is very likely. RRCA – right common carotid artery, LCCA – left common carotid artery, LSA – left subclavian artery. H. The first branch of the aortic arch in the frontal plane passes to the right and upwards; since no division within this vessel was visualized, this is the right common carotid artery (RCCA). A hyperechoic area, which could correspond to an aberrant right subclavian artery (marked [?]), is visible in the distal part of the aortic arch; however, none of the obtained images could clearly confirm this assumption (respiratory artifacts prevented Doppler flow assessment in this region)