Figure 1.
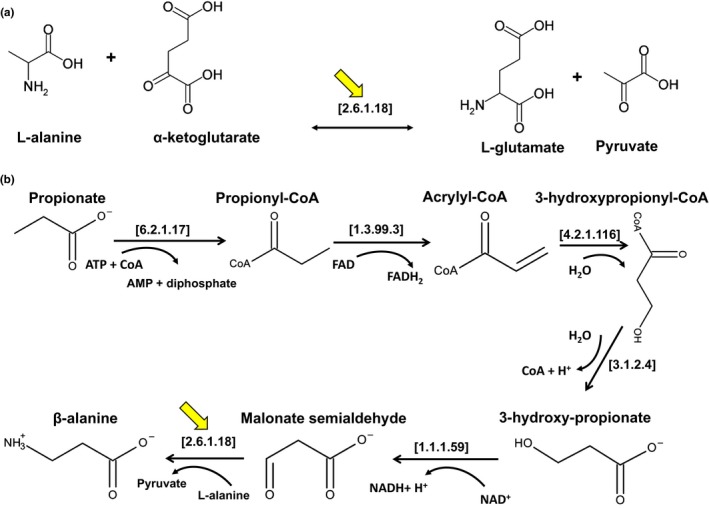
Alanine‐ and β‐alanine aminotransferase. (a) Catalysis of alanine aminotransferase (indicated by the yellow arrow). The enzyme utilizes alanine as the amino donor and α‐ketoglutarate as the amino acceptor to synthesize L‐glutamate and pyruvate in one direction. The enzyme utilizes glutamate and pyruvate as the cognate pair in the reverse direction. (b) β‐alanine synthesis from the propionate pathway. β‐Alanine aminotransferase (indicated by the yellow arrow) catalyzes the synthesis of β‐alanine and pyruvate using L‐alanine as the amino donor and malonate semialdehyde as the amino acceptor. The EC numbers of the enzymes shown in brackets correspond to the following enzymes: [6.2.1.17] = propionyl‐CoA synthetase, [1.3.99.3] = acyl‐CoA dehydrogenase, [4.2.1.116] = 3‐hydroxypropionyl‐CoA dehydratase, [3.2.1.4] = 3‐hydroxyisobutyryl‐CoA hydrolase, [1.1.1.59] = 3‐hydroxypropionate dehydrogenase, [2.6.1.18] = β‐alanine:pyruvate aminotransferase, and [2.6.1.2] = alanine aminotransferase. The yellow arrows indicate the reactions catalyzed by β‐alanine and L‐alanine aminotransferase
