Figure 3. miR-147b-VHL axis mediates drug-tolerance through impaired VHL activity.
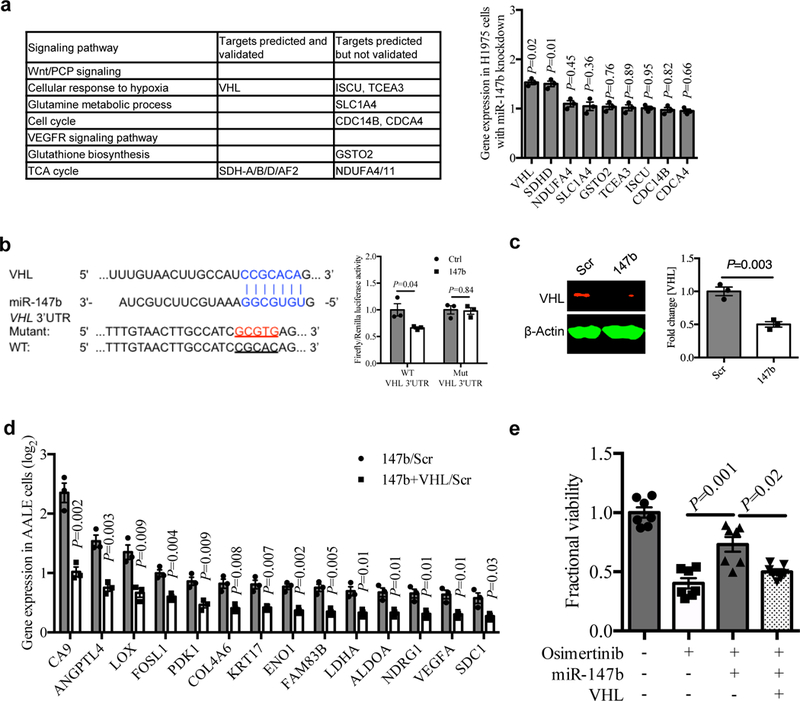
a, Left, gene candidates predicted for miR-147b by the TargetScan tool were shown in signaling pathways enriched for gefitinib-tolerance in PC9 single-cell clones in fig. 1f. Right, qRT-PCR analysis for the predicted gene candidates for miR-147b in H1975 cells with miR-147b knockdown compared with scrambled control. n=3 independent biological replicates.
b, Left, computational prediction of RNA duplex formation between miR-147b and the 3’UTR (untranslated region) of VHL mRNA. Mutations generated within the 3’UTR for the luciferase assay are shown in red. Right, dual-luciferase reporter assay in miR-147b-overexpressing AALE cells. The Firefly luciferase and Renilla luciferase activities were measured 48 hours post co-transfection with miR-147b or control vector and wild-type (WT) or mutant (Mut) VHL 3’UTR. n=3 independent biological replicates.
c, Western blot analysis and quantification of VHL in miR-147b-overexpressing AALE cells. β-Actin was used as loading control. n=3 independent biological replicates.
d, qRT-PCR analysis for fold change of hypoxia gene expression in AALE cells with miR-147b overexpression relative to scrambled control (147b/Scr) and cells with co-overexpression of miR-147b and VHL relative to scrambled control (147b+VHL/Scr). ACTB was used as endogenous control. n=3 independent biological replicates.
e, Fractional viability of HCC827 cells treated with vehicle, osimertinib (20 nM), miR-147b vector, VHL vector or combinations. The cell viability was measured on day 3. The relative cell viability treated with vehicle on day 3 was calibrated as 1. n=7 independent biological replicates.
Data are mean ± s.e.m. and were analysed with unpaired two-tailed t-test (a,b,c,d); Kruskal-Wallis test (e).
