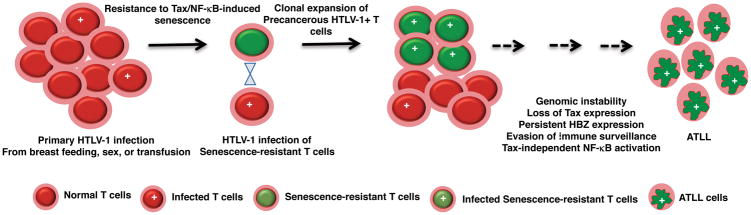
Figure 1. A model for how HTLV-1 infection progresses to ATLL.
Key events that drive ATLL development include acquisition of senescence-blocking genetic and/or epigenetic alterations by naïve T cells prior to viral infection, clonal expansion of HTLV-1-infected senescence-resistant precancerous T cells, genomic instability, loss of Tax expression, evasion of immune surveillance, persistent HBZ expression, and development of Tax-independent NF-κB activation.