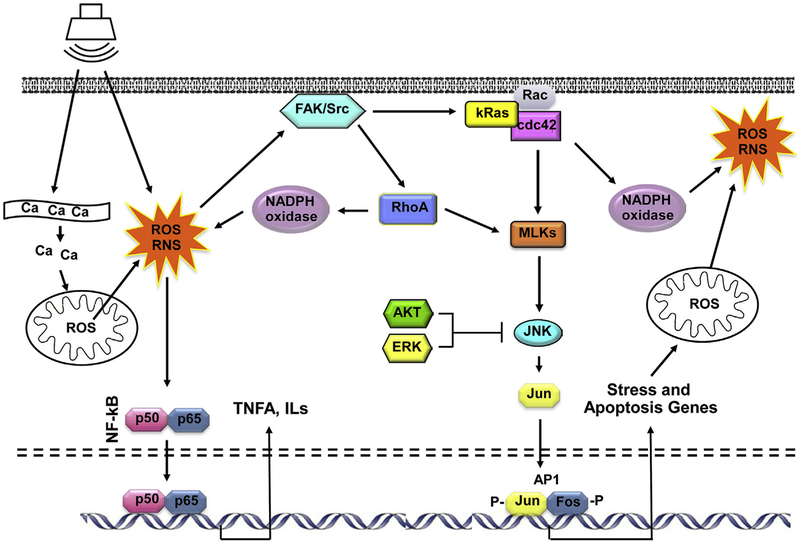
Fig. 1. Diagram illustrating damage processes and pathways thought to contribute to HC loss due to acoustic overexposure.
Noise initiates the production of ROS via release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum and/or entry from extracellular fluid, which induces release of ROS from mitochondria, and by activation of NADPH oxidases. ROS can activate NF-κB, leading to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and also κRas/cdc42/JNK pathway leading to the expression of stress and apoptosis genes. Pro-apoptotic factors further increase mitochondrial membrane permeability, leading to the release of additional ROS. The JNK pathway can be inhibited by the ERK MAPK or AKT, signaling molecules that can be activated by growth factors.