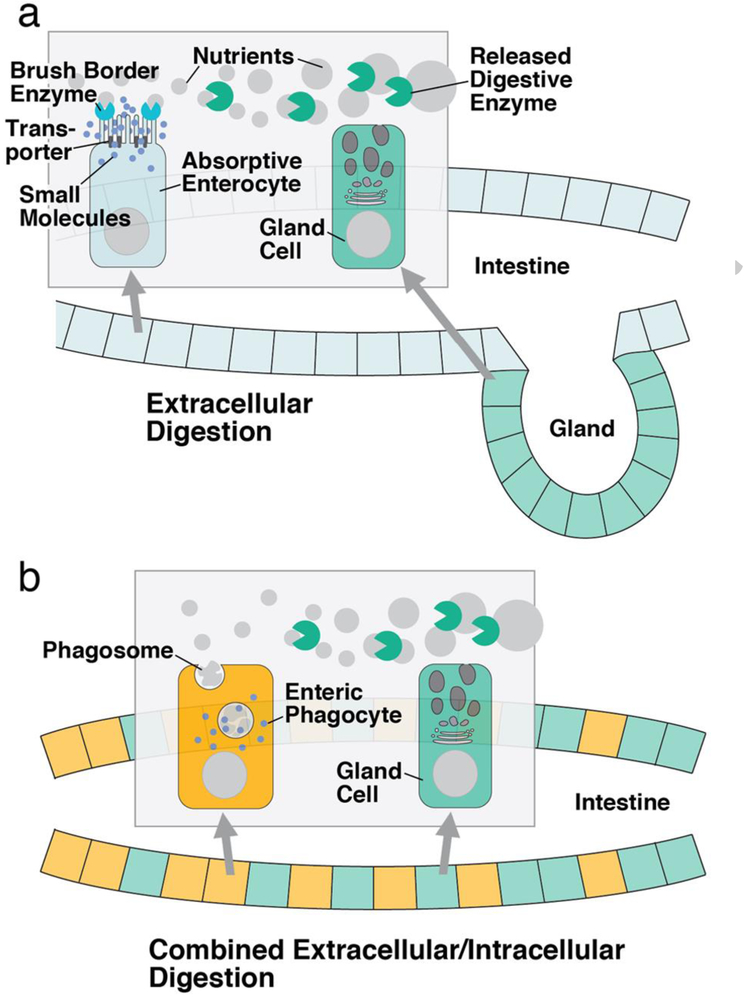
Figure 1.
Schematic depiction of extracellular digestion in the vertebrate intestine and mixed extracellular/intracellular digestion observed for most invertebrate clades. a In extracellular digestion, enzymes secreted by specialized glands (e.g., pancreas) predigest food particles into macromolecules. These are then further broken down into small molecules by a different set of enzymes produced by the enterocytes. Small molecules are absorbed by diffusion or active transport. b In combined extracellular/intracellular digestion, gland cells distributed all over the intestine predigest food material into small particles and macromolecules. These are then taken up phagocytotically and digested intracellularly by enteric phagocytes.