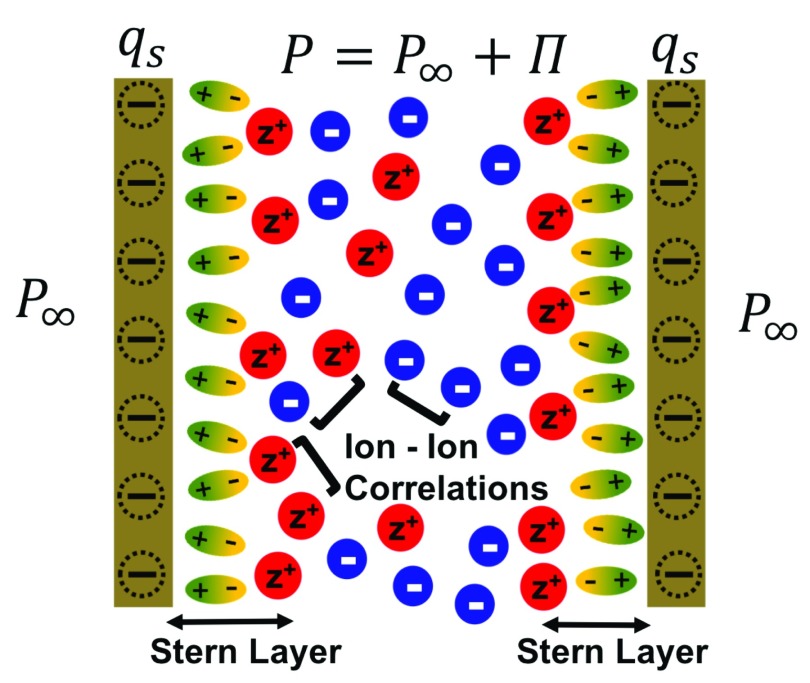
Figure 1.
Schematic of our model problem: a multivalent z:1 electrolyte is confined between two surfaces with surface charge density, qs. The disjoining pressure, Π, is defined as the difference in the pressure (P) felt between the plates due to the presence of the EDL and the pressure in the bulk reservoir (P∞). As shown here, the Stern layer which is the region closest to the charged surface is accessible only to the water molecules (depicted as ellipsoids) modeled using the hydration potential, whereas the concentration profiles of the cations (depicted as red spheres) and the anions (depicted as blue spheres) in the EDL are influenced by ion–ion correlations, described in our theory using the BSK model.