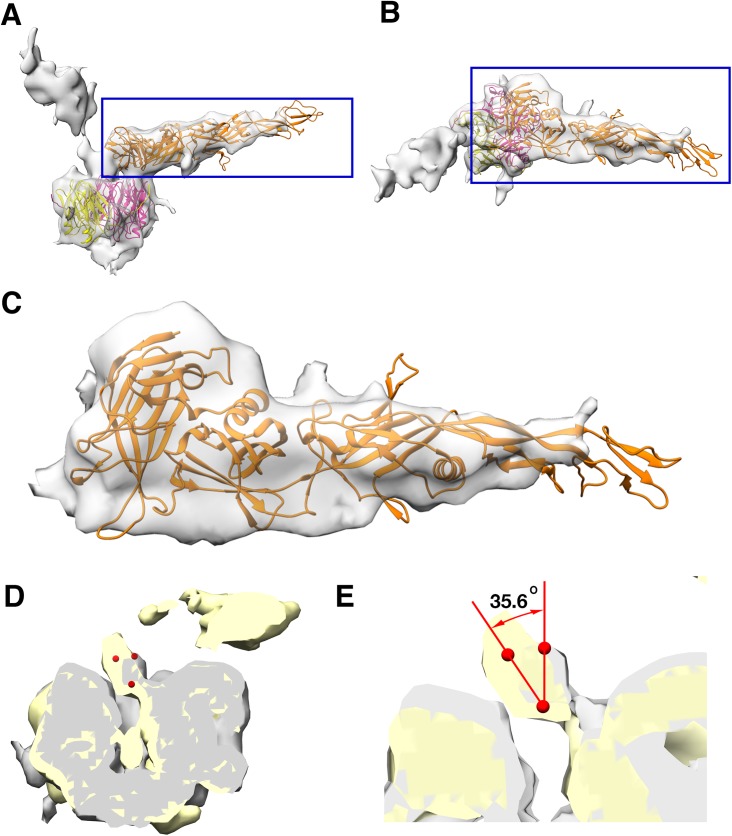
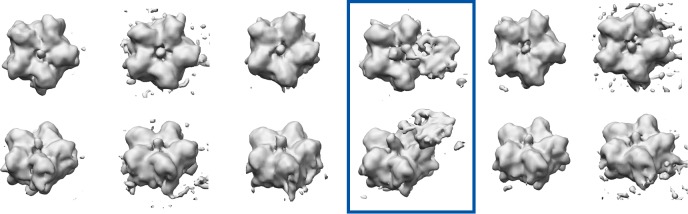
Figure 5. Monomeric P2 bound to P5.
Localized asymmetric reconstruction of the vertex complex showing the two protruding densities as gray surfaces where (A) is the side view and (B) is the top view. P2 (orange), P5 N-terminal base (bright pink) and P31 (yellow) structures fitted into these map densities. (C) Isolated CryoEM density that represents the P2 subunit. It represents the region highlighted by the blue box in (A) and (B). (D and E) Superimposed vertex maps with P2 bound (yellow) and without P2 bound (gray). In classes where P2 is bound to P5, the stalk region is nudged by ≈35.60 when compared to the classes where P2 is not bound to P5. Chimera: Volume Trace tool was used to place the red spheres in the density and Chimera: Measure Angles tool to determine the angles.