Fig. 2. Different resistance mechanisms between 1205CR1-2 and 1205CR6-7 cells.
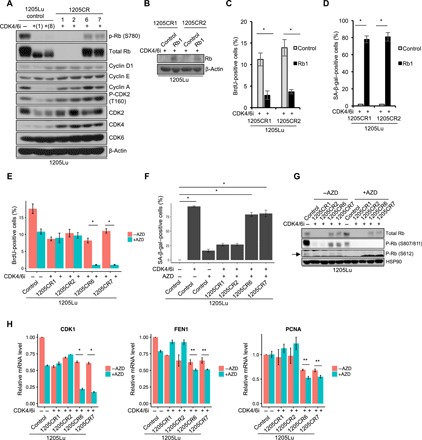
(A) Western blot analysis of lysates from 1205Lu cells treated with or without palbociclib (1 μM) for 1 or 8 days, and CR clones proliferating with palbociclib (1 μM) (1205CR1, 1205CR2, 1205CR6, and 1205CR7) using antibodies indicated on the right of the panel. (B) Western blot analysis of lysates from 1205CR1-2 cells overexpressing vehicle (control) or Rb1 using antibodies to Rb1 and β-actin. (C) 1205CR1-2 cells were subjected to BrdU incorporation for 45 min following introduction of Rb1 for 48 hours. BrdU-positive cells were determined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis. Data represent means ± SD. *P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student’s t test; n = 3). (D) Quantification of senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal)–positive cells in 1205CR1-2 with or without Rb1. Data represent means ± SD. *P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student’s t test; n = 3). (E) 1205Lu, 1205CR1, 1205CR2, 1205CR6, and 1205CR7 were subjected to a 45-min BrdU pulse following exposure to AZD5438 (AZD) treatment (0.5 μM). BrdU-positive cells were determined by FACS analysis and quantified; data represent means ± SD, *P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student’s t test; n = 3). (F) Quantification of SA-β-gal–positive cells in 1205Lu, 1205CR1, 1205CR2, 1205CR6, and 1205CR7 cells treated with AZD5438 (0.5 μM) or palbociclib (1 μM) for 8 days; data represent means ± SD, *P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student’s t test; n = 3). (G) Western blot analysis of lysates from 1205Lu, 1205CR1, 1205CR2, 1205CR6, and 1205CR7 cells after treatment of AZD5438 (0.5 μM) for 24 hours using antibodies indicated on the right of the panel. (H) qPCR analysis of samples from (G) using sets of primers for CDK1, FEN1, and PCNA. Data were normalized by GAPDH and represent means ± SD, *P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student’s t test; n = 3) and **P < 0.05 (two-tailed Student’s t test; n = 3).
