Fig. 1. Discovery of DDO-5936, an Hsp90-Cdc37 PPI inhibitor without ATPase inhibition, based on a site screening strategy involving critical residues identified at the binding interface.
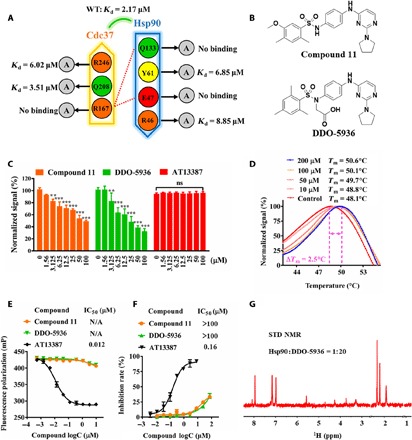
(A) Binding affinities of the WT Hsp90-Cdc37 complex and complexes with key residues mutated, determined by ITC. Hydrogen bonds are presented as red dotted lines. Data are from three independent experiments. (B) Chemical structures of compound 11 and DDO-5936. (C) Dose-dependent inhibition of the Hsp90-Cdc37 interaction by compound 11, DDO-5936, and AT13387. Twofold diluted compounds with seven concentrations were simultaneously tested by an Hsp90-Cdc37 homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) assay. The results are shown as the means ± SD, n = 3 wells, from three independent experiments. P values were calculated by pairwise comparisons to the dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) control (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001, Student’s t test). ns, not significant. (D) Thermostability of Hsp90 treated with 0, 10, 50, 100, and 200 μM DDO-5936, determined by a standard thermo shift assay. ΔTm results were obtained from the mean values of three independent assays (n = 6 wells). (E) Dose-dependent competitive binding of compound 11, DDO-5936, and AT13387 to the Hsp90 ATP binding site, determined by fluorescence polarization (FP) assays using a fluorescein isothiocyanate–geldanamycin probe. Data are presented as the means ± SD, n = 3 wells, from three independent experiments. N/A, not applicable. (F) Dose dependence of compound 11, DDO-5936, and AT13387 inhibition of Hsp90 ATPase activity. Data are presented as the means ± SD, n = 3 wells, from three independent experiments. (G) 1H saturation transfer difference (STD) NMR spectrum of 100 μM DDO-5936 binding to 5 μM Hsp90. ppm, parts per million.
