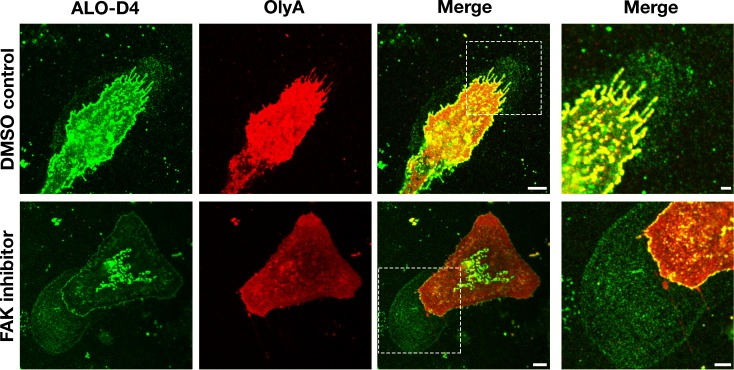
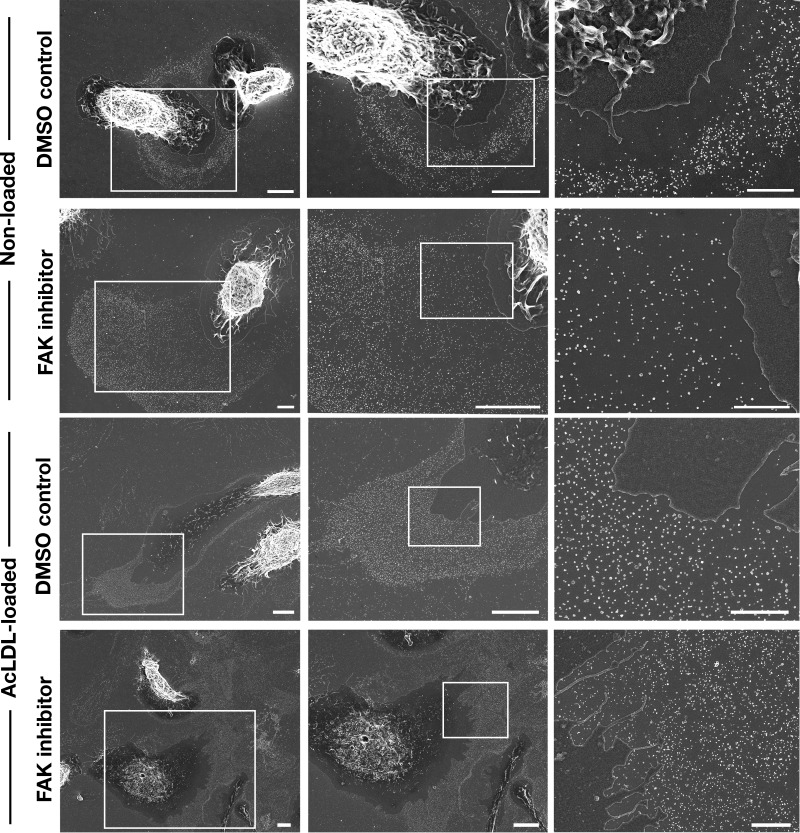
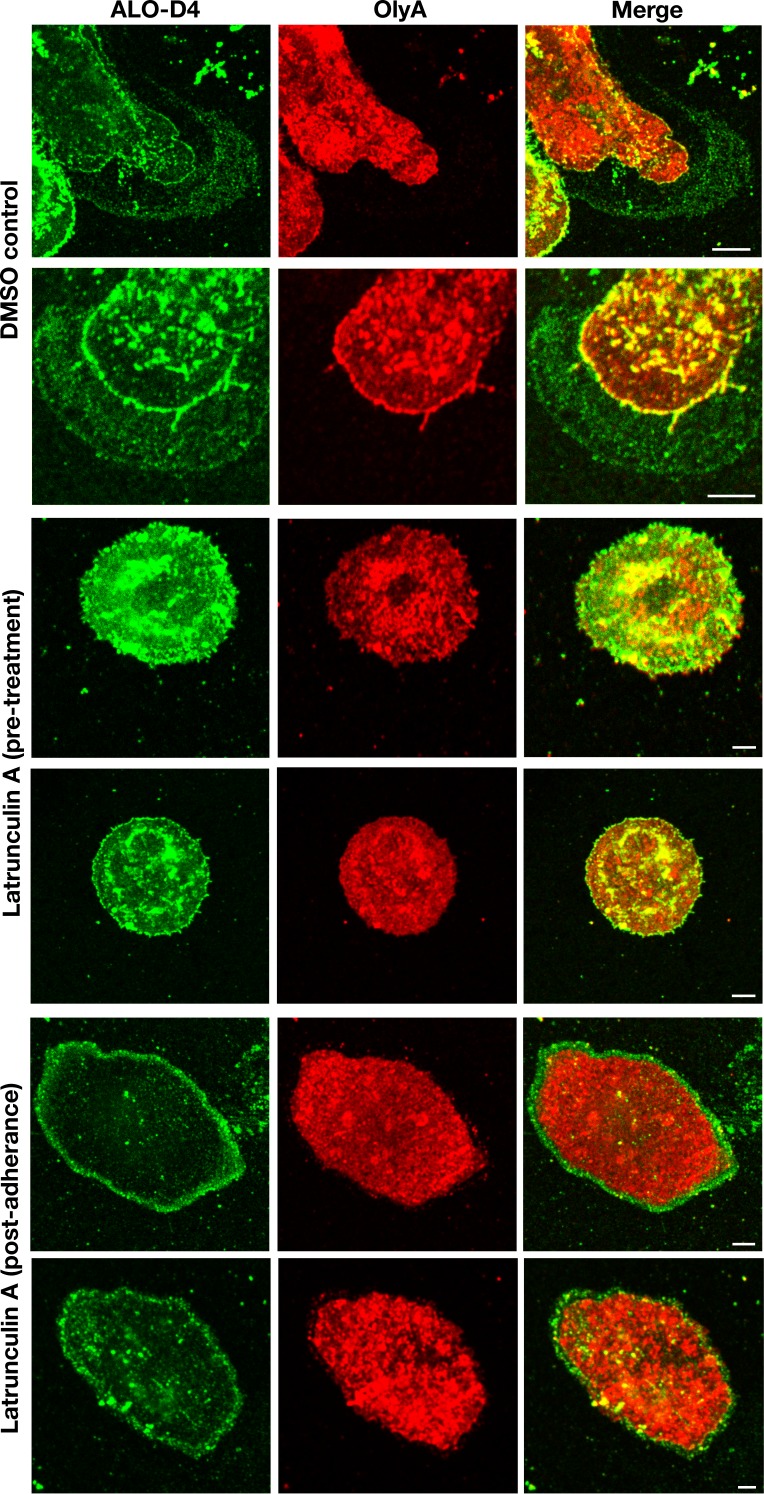
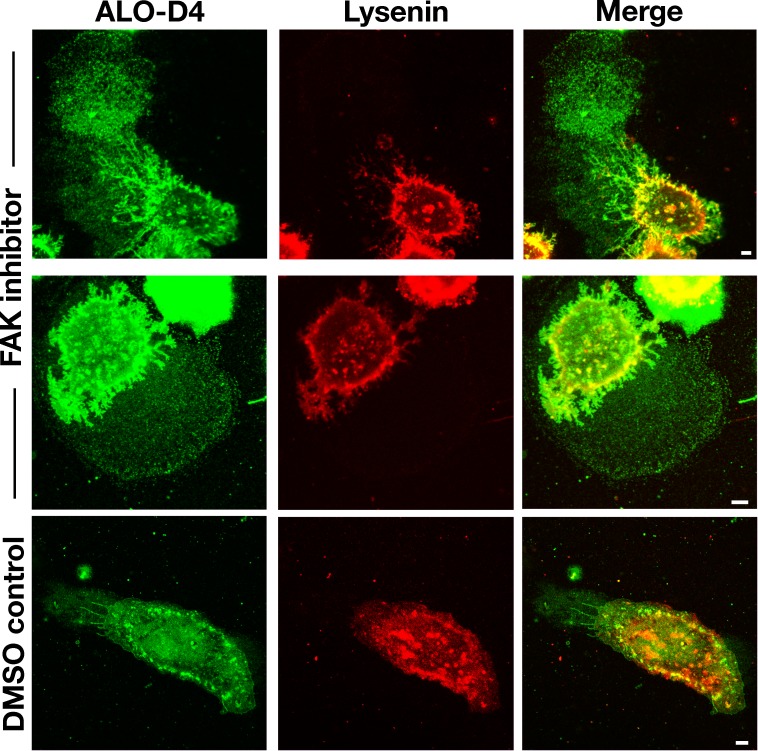
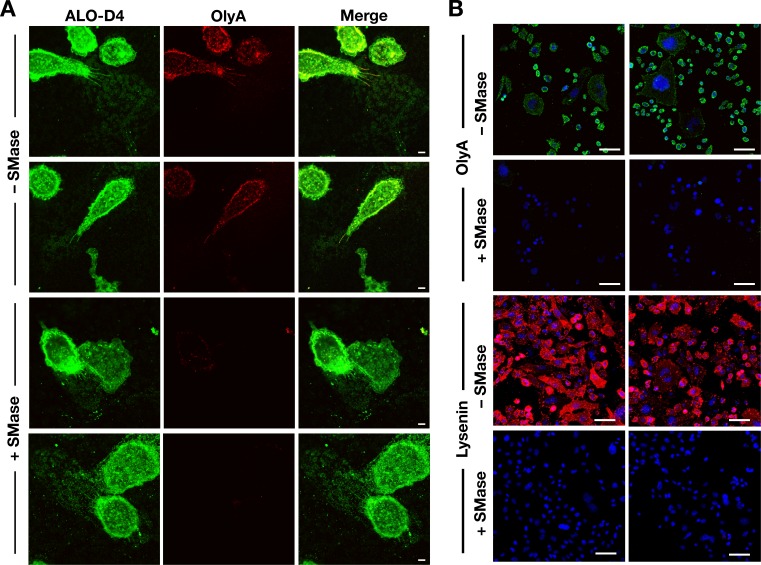
Figure 6. Particles released by mouse peritoneal macrophages onto the surrounding substrate are enriched in accessible cholesterol but not sphingomyelin-sequestered cholesterol.
Mouse peritoneal macrophages were plated onto poly-D-lysine–coated glass coverslips and incubated overnight in medium containing 10% FBS and either an FAK inhibitor (CAS 4506-66-5, 2 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) alone. On the next day, the cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor 488–labeled [15N]ALO-D4 (green), which binds to accessible cholesterol, and Atto 647N–labeled [13C]OlyA (red), which binds to sphingomyelin-bound cholesterol (both at 20 μg/ml). Cells were then washed, fixed with 3% PFA, and imaged by STED microscopy. STED images were obtained from the bottom of the macrophage (optical section of ~200 nm). The lawn of particles surrounding macrophages was readily detectable with ALO-D4, but the binding of OlyA to particles was negligible. Two independent experiments were performed; representative images are shown. Scale bar, 5 µm. Higher magnification images of the boxed regions are shown on the right. Scale bar, 2 µm.