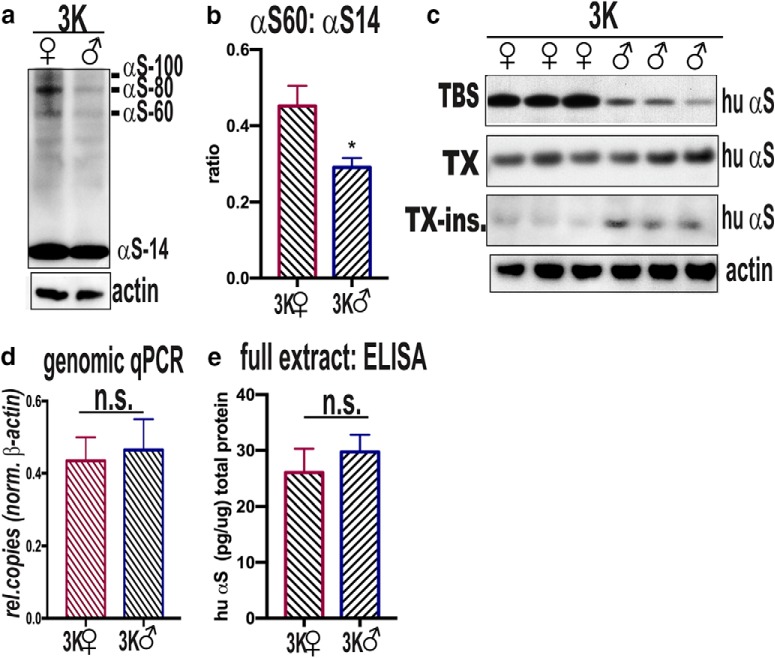
Figure 2.
Sex differences in αS solubility and T:M ratio. a, Intact cell-crosslinking of αS in cortical brain bits from 3K female and 3K male mice. Syn1 ab detects monomeric (αS14) and tetrameric (αS60) αS and probable conformers of the tetramer (αS80, αS100) (Dettmer et al., 2013). Actin serves as a control for loading. Representative WB of T:M ratio in 3K female vs. male. b, Quantitative WBs of αS monomers (∼14 kDa) and tetramers (∼60 kDa) reveal an increased T:M ratio in 3K females vs. 3K males (n = 3 mice per genotype run in 3 independent experiments). c, WBs of (non–cross-linked) sequential extractions of TBS-soluble (cytosolic), Triton X-100-soluble (membrane), and Triton X-100-insoluble full brain homogenates (15G7: hu αS) reveal increased soluble and less insoluble αS in 3K females vs. 3K males. d, Relative copy numbers by qPCR of genomic DNA with values normalized to actin. e, hu-specific αS ELISA shows equal αS protein levels in cortical brain homogenates of 6-month-old 3K male and 3K female mice (n = 3). n.s., non-significant; *p < 0.05 (unpaired two-tailed t test).