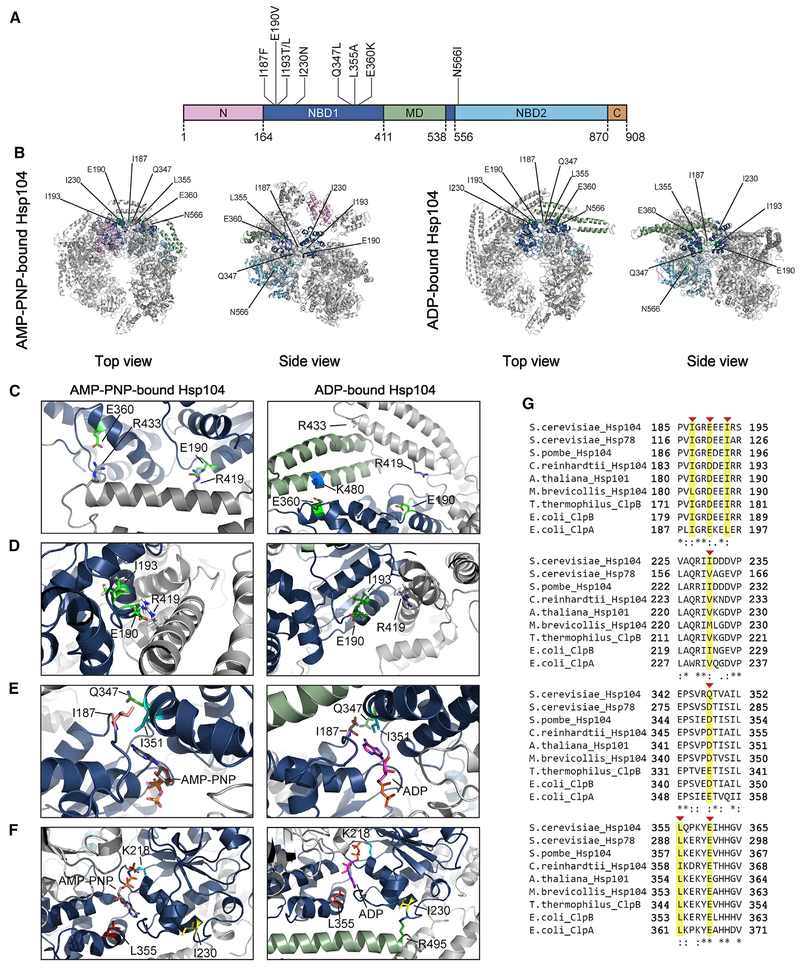
Figure 4. Location of Potentiating NBD1 and NBD2 Mutations.
(A) Domain map of Hsp104 shows the location of potentiating mutations in NBD1 (dark blue) and NBD2 (light blue). A503V is located in the MD (green). Pink, NTD; brown, CTD.
(B) Location of residues in NBD1 and NBD2 that can be mutated to potentiate Hsp104 are shown on the hexameric structure of Hsp104 bound to AMP-PNP (left; PDB: 5KNE) and bound to ADP (right; PDB: 5VY8). Protomer3(P3) is colored to denote the different domains: pink, NTD; dark blue, NBD1; green, MD; and light blue, NBD2 (as in A). P1, P2, P4, P5, and P6 are in gray.
(C–F) Zooms to show the positions of residues that can be mutated to potentiate Hsp104. (C) Top views showing the positions of E190 and E360 in P3 of the Hsp104 hexamer in AMP-PNP (left; PDB: 5KNE) and ADP (right; PDB: 5VY8). (D) Sideviews showing the positions of I193 and E190 in P3 of the Hsp104 hexamer bound to AMP-PNP (left; PDB: 5KNE) and bound to ADP (right; PDB: 5VY8). (E) Topviews showing the positions of I187 and Q347 in P3 of the Hsp104 hexamer in AMP-PNP (left; PDB: 5KNE) and ADP (right; PDB: 5VY8). (F) Side views showing the positions of I230 and L355 in P3 of the Hsp104 hexamer in AMP-PNP (left; PDB: 5KNE) and ADP (right; PDB: 5VY8).
(G) Clustal Omega (Sievers and Higgins, 2018) alignment of portions (residues 185–195, 225–235, 342–352, and 355–365) of NBD1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hsp104 with S. cerevisiae Hsp78, Schizosaccharomyces pombe Hsp104, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Hsp104, Arabidopsis thaliana Hsp101, Monosiga brevicollis Hsp104, Thermus thermophilus ClpB, Escherichia coli ClpB, and E. coli ClpA. I187, E190, I193, I230, Q347, L355, and E360 are indicated with red arrowheads and highlighted in yellow. Asterisk denotes fully conserved residue, colon denotes conservation of residues with strong similarity, and period indicates conservation of residues with weak similarity.