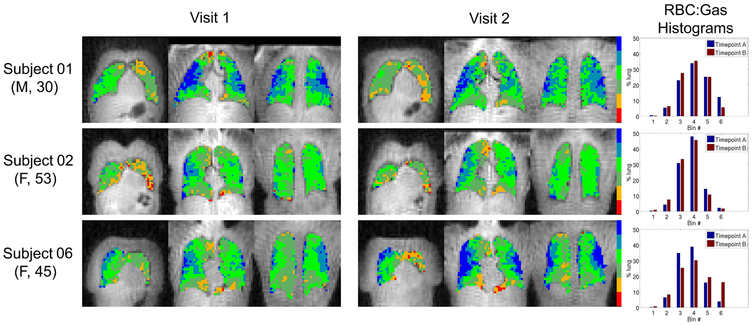
Figure 4.
Parametric maps of RBC:Gas (binned according to a reference distribution mean and standard deviation) in coronal slices from 3 different subjects at both visits (subjects and slices shown are identical to those presented in Figure 4). Lung volumes were approximately +14%, +4% and −18% different at visit 2 for subjects 01, 02 and 06, respectively. Smaller visit 2 lung volumes (e.g. Subject 06) were associated with higher visit 2 RBC:Gas, and vice versa (e.g. Subject 01). Spatial distributions of regions of relatively high and low RBC:Gas appear relatively well matched between visits. Subject numbers correspond to those in Table 1. Numerical cutoff values between RBC:Gas bins (from smallest to largest) were [−0.19, 0.07, 0.33, 0.60, 0.86].