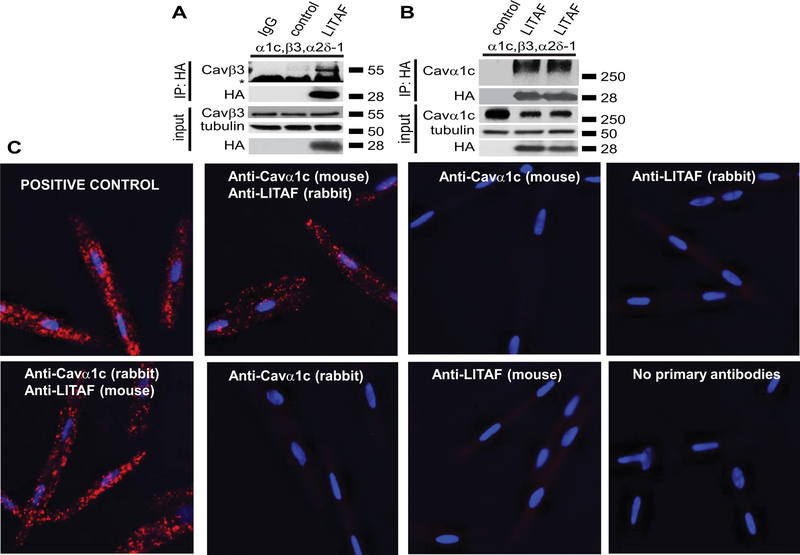
Figure 5.
Physical interaction between LITAF and LTCC in tsA201 cells and 3wRbCM. A, Immunoprecipitation (IP) of lysates from tsA201 cells transfected with plasmids for Cavα1c, Cavβ3, Cavα2δ−1, GFP, or HA-tagged LITAF using isotype control (lane 1) or HA antibody (lanes 2–3). A representative immunoblot against Cavβ3 shows an interaction between LITAF and the Cavβ3 subunit (IP panel) (the asterisk indicates the heavy chain of the IP capture antibody). Also shown is the immunopreciptated HA-LITAF protein. Input levels of Cavβ3, HA-LITAF, and tubulin are shown below. B, Immunoprecipitation (IP) of lysates from tsA201 cells transfected with plasmids for Cavα1c, Cavβ3, Cavα2δ−1, GFP, or HA-tagged LITAF using HA antibody. A representative immunoblot against Cavα1c shows an interaction between LITAF and the Cavα1c subunit (IP panel). Also shown is the immunopreciptated HA-LITAF protein. Input levels of Cavα1c, HA-LITAF, and tubulin are depicted below. C, Duo-link in situ PLA using rabbit anti-LITAF and mouse anti-Cavα1c antibodies (alternatively mouse anti-LITAF and rabbit anti-Cavα1c antibodies) in 3wRbCM, which are amenable to PLA and express detectable levels of LITAF and LTCC. Co-localization between molecules is indicated by red puncta. No puncta were detected in negative controls in which primary antibodies were omitted or only one antibody was used (rabbit anti-LITAF, mouse anti-Cavα1c, mouse anti-LITAF, or rabbit anti-Cavα1c antibodies). As positive control for the assay, a combination of rabbit polyclonal anti-Cavα2δ−1 and mouse monoclonal anti-Cavα2δ−1 was used to detect endogenous Cavα2δ−1. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).