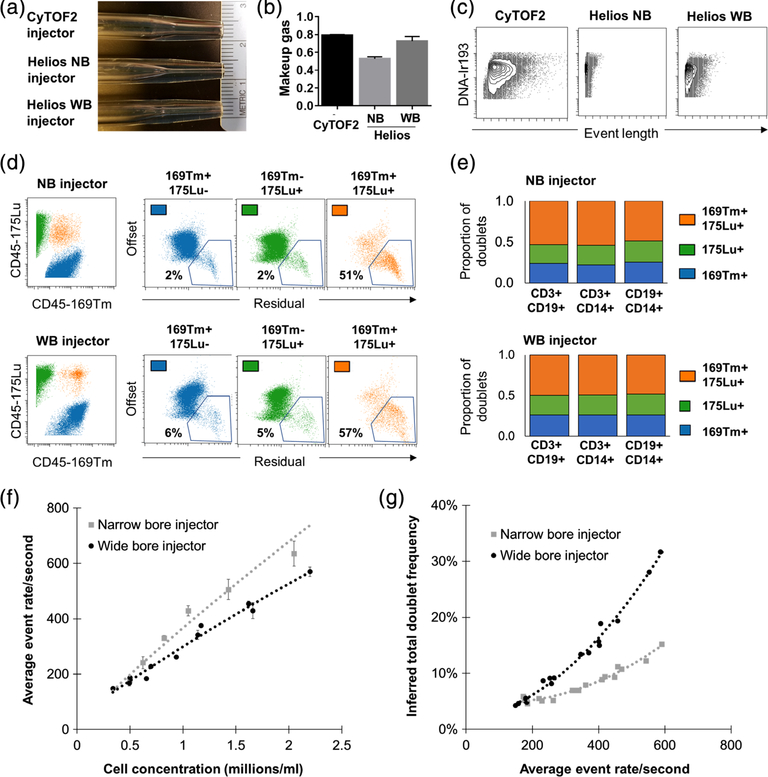
Figure 3.
Acquisition characteristic of the narrow and wide bore injector Helios configurations. (A) Photographs of the CyTOF2, Helios NB, and Helios WB injectors showing the intermediate internal bore diameter of the WB injector. (B) Average optimal makeup gas (L/min) with each of the injectors as determined by tuning with a fixed nebulizer gas rate of 0.17 l/min. (C) Representative event lengths for parallel sample aliquots acquired with each of the injectors. (D-G) Two aliquots of the same PBMC sample were barcoded with 169Tm and 175Lu-conjugated CD45-antibodies, which were combined at an equal ratio and acquired in parallel on the same Helios instrument using either the WB or NB injector. (D) 169Tm + 175Lu + events were identified as known cross sample doublets and were confirmed to exhibit higher residual and offset Gaussian parameter values. (E) The relative proportion of CD3 + CD19+ (T cell-B cell), CD3 + CD14+ (T cell-monocyte), and CD19 + CD14+ (B cell-monocyte) doublets within the 169Tm + 175Lu + doublet population confirmed that the total doublet frequency could be accurately estimated as 2× the measured frequency of CD45 169Tm + 175Lu + doublets. (F) Average event rate for samples acquired at a given cell concentration using each injector. (G) Calculated total doublet frequency in relation to event acquisition rate using each injector. Data represent values from three replicate acquisitions of the same cell suspension diluted at each cell concentration and acquired on a single Helios instrument. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]