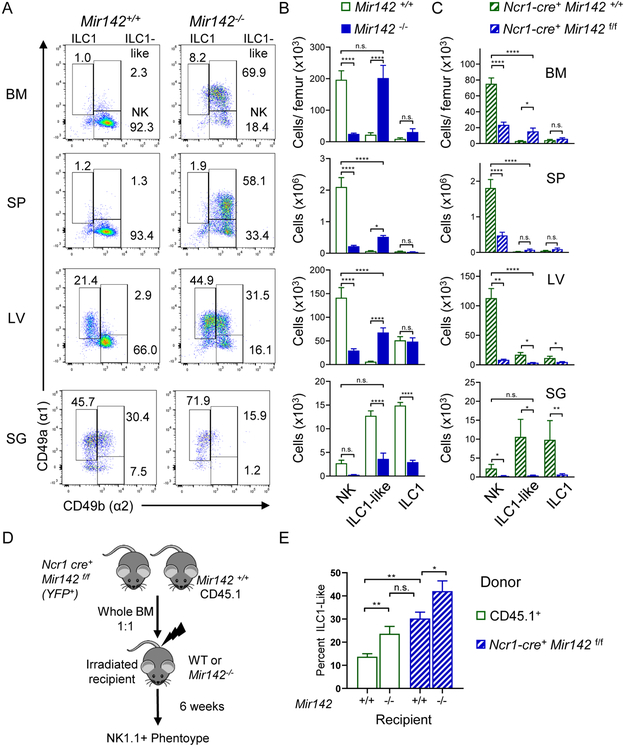
Figure 2. miR-142-deficient mice display altered, tissue-specific type-1 ILC compartment.
The CD3−NK1.1+NKp46+ compartment of Mir142+/+ (open green) and Mir142−/− (filled blue) mice was assessed for CD49a and CD49b by flow cytometry. (A) Representative flow plots of CD3−NK 1.1 +NKp46+ cells. (B) Total number of NK cells (NK, CD49a−CD49b+), ILC1-like (CD49a+CD49b+), and ILC1s (CD49a+CD49b−) within the indicated tissues. Summary from >3 independent experiments with > 10 mice per group. (C) Total numbers of NK, ILC1-like, and ILC1 cells within control (Ncr1-cre+ Mir142+/+) and ILC-specific miR-142-deficient (Ncr1-cre+ Mir142f/f) mice, cells gated on CD3−NK1.1+NKp46+ YFP+. (D) Experimental Schema. BM from control and Ncr1-cre+ Mir142f/f mice were transferred into irradiated recipients and spleens assessed 6 weeks later. (E) Summary data showing the percent of ILC1-like cells from CD3-NK1.1+NKp46+ CD45.1+ (WT) or YFP+ (Mir142f/f) within the indicated recipient mice. Data from 2-3 independent experiments, N=7-10 mice, compared using T-test or Mann-Whitney corrected for multiple comparisons, when appropriate. See also Figure S2.