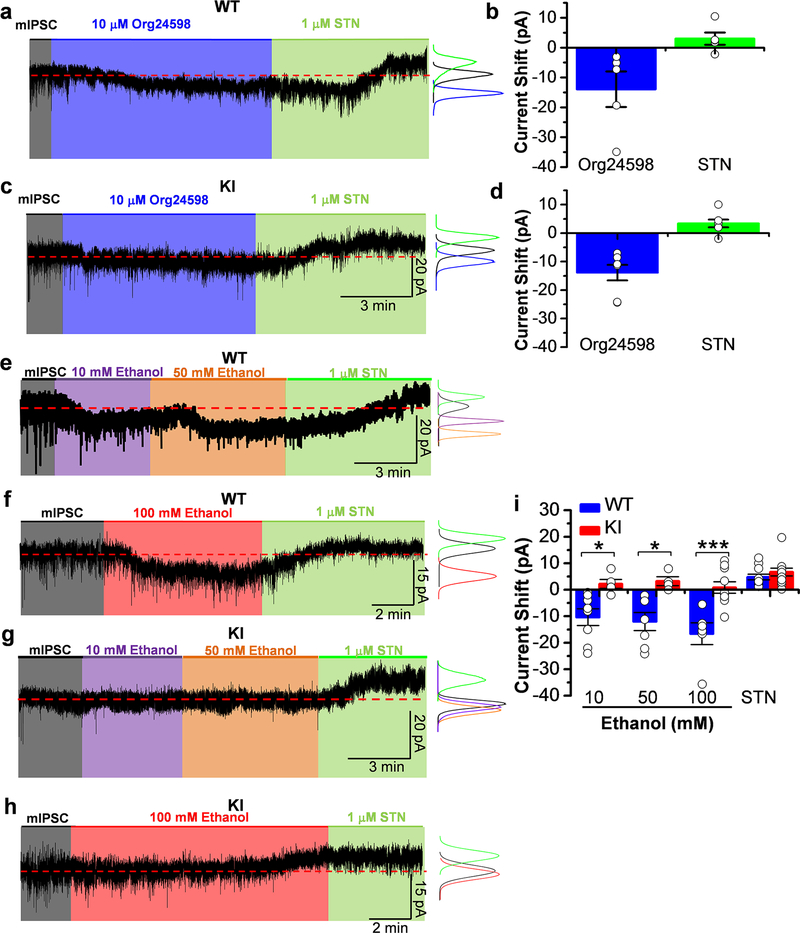
Figure 2. Presence of tonic inhibitory currents mediated by GlyRs that are sensitive to ethanol in WT nAc.
a and c) Representative electrophysiological trace from WT and KI neuron in the presence of 10 μM Org24598 (blue shaded area) and 1 μM STN (green shaded area). The red dotted line indicates the baseline. The histogram graph shows the analysis of the trace. Org24598 induced an inward current in nAc. STN abolished mIPSCs and produced a positive shift in the holding current in both genotypes. b and d) The graph summarizes the effects of Org24598 and STN on glycine tonic currents from WT and KI neurons. (n=5 neurons from 3 WT mice and n=7 neurons from 4 KI mice). e) Representative electrophysiological trace from a WT neuron in the presence of 10 (purple shaded area) and 50 mM ethanol (orange shaded area) and 1 μM STN (green shaded area). The red dotted line indicates the baseline. The histograms show the analysis of the trace. Low and high ethanol concentrations increased GlyR-mediated currents in the nAc. This effect was abolished by STN. f) Representative electrophysiological trace from a WT neuron in the presence of 100 mM ethanol (red shaded area) and 1 μM STN (green shaded area). The red dotted line indicates the baseline. The histogram graph shows the analysis of the trace. Ethanol increased the GlyR-mediated current in the nAc. This effect was abolished by STN. g) Representative electrophysiological trace from a KI neuron in the presence of 10 (purple shaded area) and 50 mM ethanol (orange shaded area) and 1 μM STN (green shaded area). The red dotted line indicates the baseline. The histogram graph shows the analysis of the trace. GlyR-mediated tonic currents in KI were not affected by low and high concentrations of ethanol. STN produced a positive shift in the holding current. h) Representative electrophysiological trace from a KI neuron in the presence of 100 mM ethanol (red shaded area) and 1 μM STN (green shaded area). The red dotted line indicates the baseline. The histogram graph shows the analysis of the trace. Ethanol did not affect the holding current; however STN abolished the mIPSCs and produced a positive shift in the holding current. Tonic currents in KI neurons were resistant to ethanol effects. i) The graph summarizes the effects of 10, 50 and 100 mM ethanol and STN on WT and KI glycine tonic currents, showing an increase in tonic current only in WT neurons (p=5.189E−7, F1,36=37.1487). Data are mean ± SEM. n=7 neurons from 3 WT mice and n=5 neurons from 2 KI mice for 10 and 50 mM ethanol and n=6 neurons from 3 WT mice and n=10 neurons from 4 KI mice for 100 mM ethanol. ns p>0.05, *p<0.05, ***p<0.001. Two-way ANOVA, Tukey test.