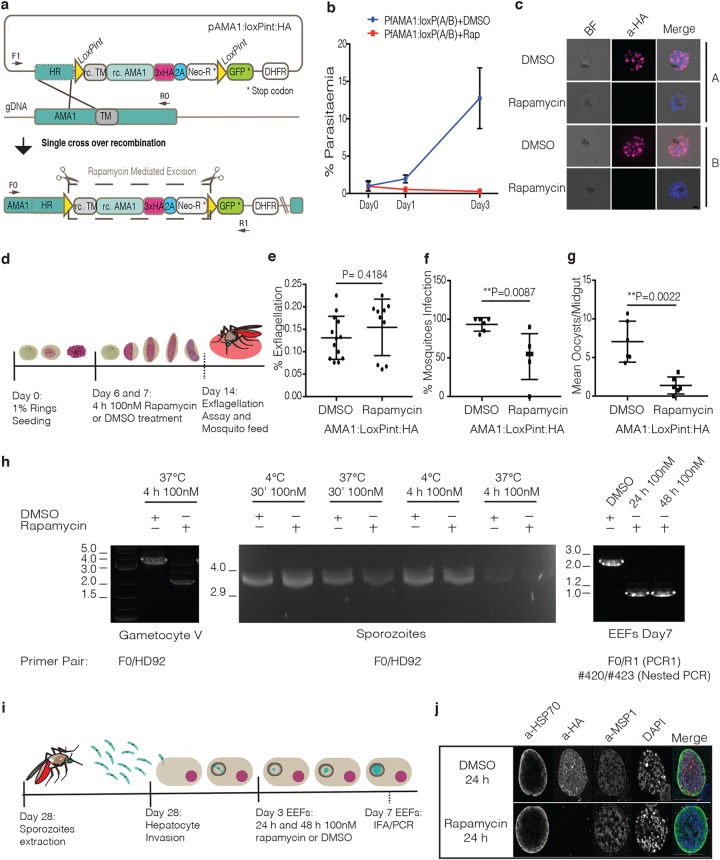
FIG 2.
Characterization of rapamycin-mediated excision efficiency of the AMA1 gene in the NF54::DiCre line across P. falciparum life cycle. (a) Description of the strategy used to make the AMA1 conditional knockout (KO) line (AMA1:loxPint:HA) and the primers used to confirm integration. The rescue plasmid contains a recodonized version of the C-terminal ama1 gene (rc. AMA1), followed by a triple-HA (3xHA), T2A peptide (2A), and neomycin resistance cassette (Neo-R), flanked by loxPints. A GFP cassette is used to monitor rapamycin-mediated excision events. (b) Growth curve comparing DMSO- and rapamycin-treated asexual parasites of two independent transfections (populations A and B) representing two independent experiments. (c) Immunofluorescence analysis of DMSO- and rapamycin-treated asexual parasites from populations A and B using anti-HA antibody (α-HA) to check for efficient rapamycin-induced excision. (d) Representation of the experimental workflow to test rapamycin-induced AMA1 KO during early sexual development. (e) Exflagellation assays comparing male gametocyte exflagellation centers of DMSO- versus rapamycin-treated gametocytes (percent total mature gametocytes). The data points represent the values for technical replicates from two independent experiments. (f) A. stephensi infection rates comparing DMSO- versus rapamycin-treated AMA1:loxPint:HA gametocytes. Each data point corresponds to the value of an independent experiment. (g) Average number of oocysts per mosquito midgut from DMSO- and rapamycin-treated AMA1:loxPint:HA parasites. Each data point corresponds to the value of an independent experiment. (h) PCR analysis comparing DMSO- versus rapamycin-treated parasite genomic DNA extracted from different developmental stages. Gametocytes were treated sequentially on days 6 and 7 after induction, sporozoites were treated either for 30 min (30’) or 4 hours (4h) at either 4°C or 37°C, and EEFs were treated for 24 h or 48 h. The sequences of the primers used are shown in Table S1. (i) Description of DMSO and rapamycin treatment point for conditional gene deletion during hepatocyte development. (j) Immunofluorescence analysis of EEFs on day 7 after hepatocyte infection comparing DMSO versus rapamycin treatment. All P values were calculated by the Mann-Whitney t test.