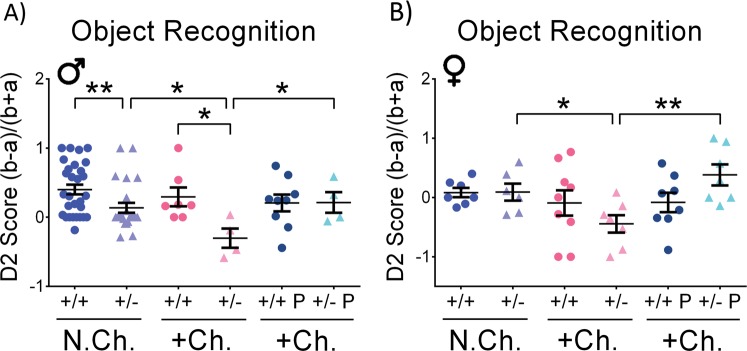
Fig. 2. Adnp+/+ mice display intact cognitive phenotype under stress-challenge, as opposed to Adnp+/− mice: PACAP treatment ameliorates.
Two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test was performed (males (M): N.Ch. Adnp+/+ N = 29; N.Ch. Adnp+/− N = 24; +Ch. Adnp+/+ N = 7; +Ch. Adnp+/− N = 4; +Ch. Adnp+/+ PACAP N = 9; +Ch. Adnp+/− PACAP N = 4; females (F): N.Ch. Adnp+/+ N = 7; N.Ch. Adnp+/− N = 6; +Ch. Adnp+/+ N = 9; +Ch. Adnp+/− N = 7; +Ch. Adnp+/+ PACAP N = 8; +Ch. Adnp+/− PACAP N = 7). a In stress-challenged male mice, main genotype (F(1,20) = 4.444, p = 0.048) and interaction (F(1,20) = 4.628, p = 0.044) effects were found, with significant differences between PACAP- and vehicle-treated Adnp+/− mice (*p < 0.05), and Adnp+/+ vs. Adnp+/− mice (**p < 0.01). In vehicle-treated male mice, main genotype (F(1,60) = 12.085, p < 0.001) and challenge (F(1,60) = 4.873, p = 0.031) effects were found, with significant differences between non-challenged Adnp+/+ and Adnp+/− mice (*p < 0.05), and challenged vs. non-challenged Adnp+/− mice (*p < 0.05). b In stress-challenged female mice, main treatment effect was found (F(1,27) = 4.392, p = 0.046), with a significant difference between PACAP- and vehicle-treated Adnp+/− mice (**p < 0.01). In vehicle-treated female mice, main challenge effect was found (F(1,25) = 4.419, p = 0.046), with a significant difference between stress-challenged and non-stressed Adnp+/− mice (*p < 0.05)