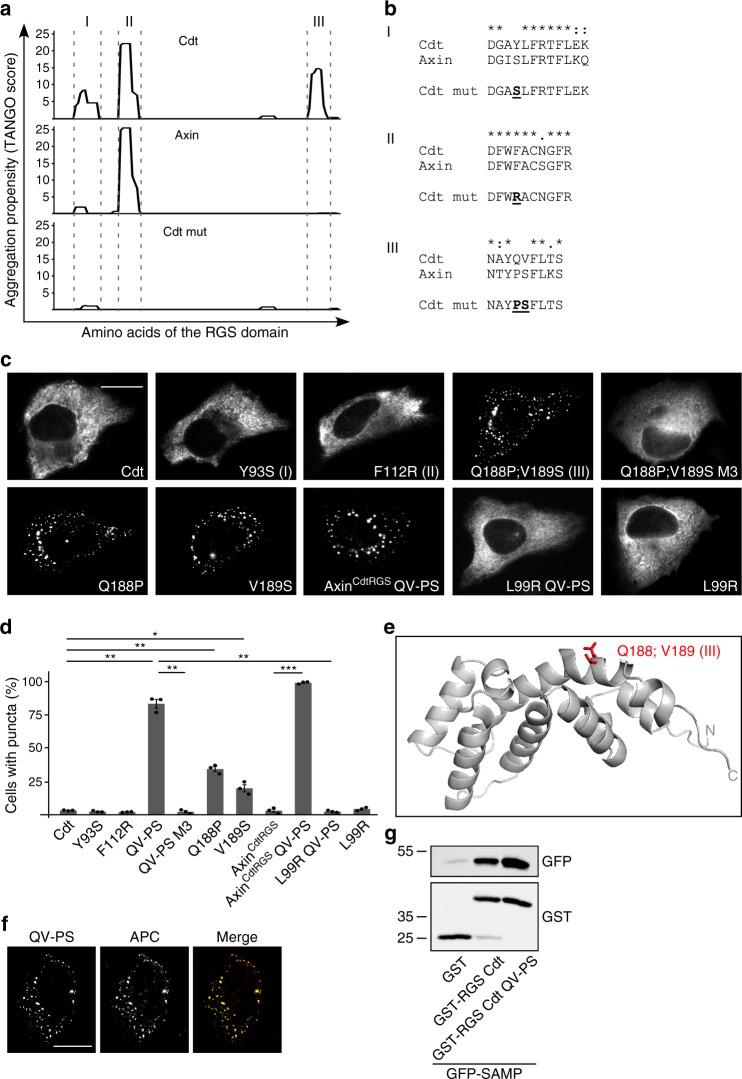
Fig. 2.
An aggregation site within the RGS domain prevents conductin polymerization. a Aggregation propensity score calculated by the TANGO algorithm for amino acids in the RGS domains of conductin (Cdt), axin, and mutated conductin (Cdt mut). b Clustal Omega alignments of conductin and axin sequences for the three aggregation sites predicted in a. Identity (*) and conservation between amino acid groups of strongly (:) and weakly (.) similar properties are indicated38. Mutated key residues are highlighted. c GFP fluorescence in U2OS cells transfected with indicated GFP-tagged constructs. Scale bar: 20 µm. d Percentage of transfected cells showing puncta formation of indicated constructs. Per construct, 1500 cells of three independent experiments as in c were analyzed. Results are mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). e 3D structural model of the conductin RGS domain calculated by SWISS-MODEL using the crystal structure 1DK8 of the highly similar axin RGS domain (Fig. 1a) as a template41,42. The Global Model Quality Estimate (GMQE) reached 0.80. Amino acids mutated within aggregation site III are indicated in red. N- and C-terminus are labeled with N and C, respectively. f Immunofluorescence staining of APC (red) in U2OS cells transfected with GFP-tagged conductin QV-PS (green) together with APC. Scale bar: 20 µm. g Western blotting for indicated proteins after GST-pull down from an extract of HEK293T cells expressing GFP-SAMP which was aliquoted and supplemented with equal amounts of either GST, GST-RGS Cdt, or GST-RGS Cdt QV-PS. Source data are provided as a Source Data file